World
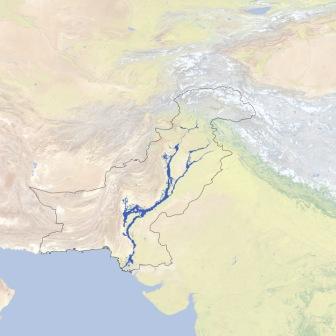
Flood extent in Pakistan - Updates from NASA Earth Observatory
Posted on 26 Apr, 2011 11:41 AM
La Niña conditions increased atmospheric moisture and an unusual pattern in the jet stream trapped rainy weather over the country. According to the Pakistan Meteorological Department, nationwide rain totals were 70 percent above normal in July, and 102 percent above normal in August.
Peel potential - Bananas can filter heavy metals from water - Article from Down to Earth
Posted on 25 Apr, 2011 12:26 PMGlobal equatorial sea-surface temperatures over the last 150,000 years: An update from foraminiferal elemental analysis – A paper in Current Science
Posted on 25 Apr, 2011 10:21 AMSolar insolation changes are amongst various factors that affect sea-surface temperature, which in turn modulate global climate. Out of all the oceanic regions, equatorial region receives the maximum solar insolation and thus is the locale for the warmest waters. However, how the equatorial sea-surface temperature affects global climate, is still not clear.
Certificate of Advanced Studies in Management of Development Projects – EPFL - Apply by 31st July, 2011
Posted on 22 Apr, 2011 06:14 PMWith more than 250 laboratories and research groups, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne) is one of Europe’s most innovative and productive technology institutes.
To help professionals to adapt to today’s globalized world, situations and promote an interdisciplinary and multicultural approach to these problems, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), Lausanne with the support of the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore, is organizing a Certificate of Advanced Studies in Management of Development Projects (MaDePro) targeted at project managers, engineers, architects, social scientists and other equivalent university graduates. The program is based on three different aspects: knowledge, practice and skills.
Groundwater: From mystery to management - An article by TN Narasimhan
Posted on 22 Apr, 2011 12:07 PMGroundwater has been used for domestic and irrigation needs from time immemorial. It is a component of the hydrological cycle, vital for human sustenance. Unlike surface water, groundwater cannot be readily observed. Consequently, it was long considered to be mysterious or even occult in nature, influencing legal decisions relating to groundwater ownership and use.
Adapting to the global groundwater crisis - Its usage needs to be regulated and monitored
Posted on 22 Apr, 2011 12:03 PMThe global groundwater crisis centers on withdrawals notably exceeding short term renewable storage. The current global groundwater crisis reflects the fact that over the past century, groundwater withdrawal has grown to exceed natural renewable groundwater storage. The single most important cause is the deep well turbine pump. Groundwater depletion is very high in both the United States and India.
The Water Footprint Assessment Manual: Setting the global standard – Methods for water footprint accounting by the Water Footprint Network
Posted on 21 Apr, 2011 10:14 PM This book by Earthscan contains the global standard for ‘water footprint assessment’ as developed and maintained by the Water Footprint Network (WFN). It shows how water footprints are calculated for individual processes and products, as well as for consumers, nations and businesses. It also includes methods for water footprint sustainability assessment and a library of water footprint response options.
This book by Earthscan contains the global standard for ‘water footprint assessment’ as developed and maintained by the Water Footprint Network (WFN). It shows how water footprints are calculated for individual processes and products, as well as for consumers, nations and businesses. It also includes methods for water footprint sustainability assessment and a library of water footprint response options.
A shared standard on definitions and calculation methods is crucial given the rapidly growing interest in companies and governments to use water footprint accounts as a basis for formulating sustainable water strategies and policies. The current manual is an updated, revised and expanded version of Water Footprint Manual: State of the Art 2009, published by the WFN in November 2009 (Hoekstra et al, 2009a). This new edition has been produced after intensive consultations with partners and researchers worldwide. Directly following the publication of the Water Footprint Manual, all partners of the WFN were invited to provide feedback on the manual.
Youth forum on climate actions and mountain issues - The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), 8th – 12th August, 2011, Kathmandu, Nepal
Posted on 19 Apr, 2011 11:09 AMOrganizer: The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Venue: ICIMOD headquarters, Kathmandu, Nepal
Description:
The overall objective of the Youth Forum is to celebrate International Year of Youth 2011/12 and International Youth Day, 12 August, through continuation of series of activities started in 2008 to build the next generation leadership in sustainable mountain development and climate change adaptation in ICIMOD Regional Member Countries (RMCs) and beyond, especially in the context of upcoming UNFCCC CoP 17 and Rio+20 meeting.
Call for applications for DFID-ESRC Growth Programme - Apply by 26th May, 2011
Posted on 18 Apr, 2011 11:24 AMThe Department for International Development (DFID) and the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) are partnering in a new programme on economic growth in developing countries. The DFID/ESRC Growth Programme (DEGP) will fund world class scientific research on issues relating to inclusive economic growth in Low Income Countries (LICs), with high potential for impact on policy and practice.
Paddy and water management with the System of Rice Intensification (SRI) – A special issue of the journal "Paddy and Water Environment"
Posted on 17 Apr, 2011 10:30 AM This brings together the results of formal research on SRI in a number of countries (Part I) and also reports on initiatives by government agencies, NGOs, universities, or the private sector, bringing knowledge of SRI to farmers in a wide range of agroecological circumstances (Part II). It has six articles and nine technical reports from Afghanistan, China, the Gambia, Kenya, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Mali, Pakistan, Panama, and Thailand as well as several review articles.
This brings together the results of formal research on SRI in a number of countries (Part I) and also reports on initiatives by government agencies, NGOs, universities, or the private sector, bringing knowledge of SRI to farmers in a wide range of agroecological circumstances (Part II). It has six articles and nine technical reports from Afghanistan, China, the Gambia, Kenya, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Mali, Pakistan, Panama, and Thailand as well as several review articles.
The System of Rice Intensification (SRI), developed in Madagascar almost 30 years ago, modifies certain practices for managing plants, soil, water, and nutrients with the effect of raising the productivity of the land, labor, and capital devoted to rice production. Certain production inputs are reduced—seeds, inorganic fertilizer, water, and fuel where water is pumped—with increased yield as a result.