Research Papers
Sea level rise – Impact on major infrastructure, ecosystems and land along the Tamil Nadu coast – A report by IFMR and IIT Madras
Posted on 24 Aug, 2011 03:53 PM This report by Institute of Financial Management and Research (Madras) and Indian Institute of Technology (Madras) deals with the impact of sea level rise on major infrastructure, ecosystems and land along the Tamil Nadu coast.
This report by Institute of Financial Management and Research (Madras) and Indian Institute of Technology (Madras) deals with the impact of sea level rise on major infrastructure, ecosystems and land along the Tamil Nadu coast.
The Tamil Nadu coastline is about 1,076 km, with thirteen coastal districts, and it forms a fairly large contiguous and narrow coastal strip dotted with fragile ecological features and rampant development activities. There are major, existing and proposed, economic and infrastructure developments, including ports, power plants, highways and even airports, which are being planned very close to the shoreline along India’s coast.
Scope, structure and processes of National Environment Assessment and Monitoring Authority – A draft report of the Ministry of Environment and Forests
Posted on 24 Aug, 2011 01:10 PMThis report by the Indian Institute of Technology (Delhi) for the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF) deals with the scope, structure and processes of the proposed National Environment Assessment and Monitoring Authority (NEAMA). The findings and recommendations of the project are based on an analysis of various research and committee reports, a critical review of the implementation of EIA notification 2006, CRZ notification 1991 & CZM Notification 2010, and a review of the international practices.
Blue harvest – Inland fisheries as an ecosystem service – A report by UNEP
Posted on 24 Aug, 2011 11:34 AM This report by United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reviews the importance of inland fisheries as an ecosystem service, the pressures upon them, and management approaches to sustain them and thus helps inform future approaches to conservation and management of freshwater ecosystems.
This report by United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reviews the importance of inland fisheries as an ecosystem service, the pressures upon them, and management approaches to sustain them and thus helps inform future approaches to conservation and management of freshwater ecosystems.
There is an urgent need for major investment in policy and management approaches that address the direct and indirect drivers of aquatic ecosystem degradation and loss of inland fisheries taking into account their role in sustainable development and human well being. The UNEP Ecosystem Management Programme (UNEP-EMP) provides an effective framework for pursuing this challenge.
Sanitation as a business - A new spin on the challenge of sanitation operation and maintenance - A paper by Water for People
Posted on 24 Aug, 2011 11:34 AMThis paper published by the Water for People describes Sanitation as a Business, an innovative approach to operation and maintainance challenges in household sanitation improvements, by describing the case of the implementation of the approach in the context of Malawi, by Water for People. The paper argues that programs that build latrines have consistently struggled to have impact or reach scale, and have often distorted the market environment in ways that have undermined future sanitation development.
The paper emphasises the relevance of this approach in the context of developing countries such as India by stating that the world would not be able to achieve even half of the Millennium Development Goals for sanitation at current rates of installation and consequently is projected to miss the sanitation MDG by more than 700 million people. Among the twenty two percent of those without access to improved sanitation, the greatest challenge remains in Asia and India in particular.
Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission – Report of an evaluation study by the Planning Commission (2010)
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 10:17 PMThis evaluation study report by the Programme Evaluation Organisation, Planning Commission attempts to document the major achievements in rural water services under Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission. It does so by assessing the extent of coverage and access to improved services in the rural areas.
Challenges of sustainable water quality management in rural India - Current Science
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 04:51 PM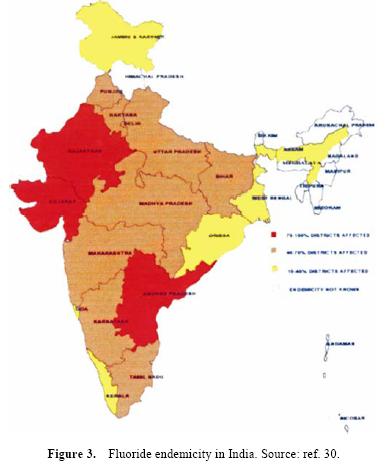 The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
While access to drinking water in India has increased over the past decade, the tremendous adverse impact of unsafe water on health continues. It is estimated that about 21% of communicable diseases in India are water related.
Although some degree of intervention in terms of chlorination and monitoring of water quality exists in major cities and towns, rural India, which constitutes the bulk (70%) of the population, is usually deprived of such interventions. The population in rural India is mainly dependent on the groundwater as a source of drinking water. As a quality concern the groundwater is often found to be contaminated with fluoride, arsenic, iron and salts. In recent years, fluorosis has emerged as major public health issue in rural India.
Sanitation - The hygienic means of promoting health - Indian Journal of Public Health
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 11:10 AMThis article published in the Indian Journal of Public Health highlights the importance of sanitation as hygienic means of dealing with health of populations and presents the history and the definition of sanitation and highlights t
Biomass for sustainable development - Lessons for decentralized energy delivery in India – A report by World Bank
Posted on 22 Aug, 2011 07:55 PM It presents a summary of recommendations for enhancing the effectiveness of energy service delivery through a decentralized program, which currently finds a critical place in the Government‘s energy policies and electrification targets.
It presents a summary of recommendations for enhancing the effectiveness of energy service delivery through a decentralized program, which currently finds a critical place in the Government‘s energy policies and electrification targets.
The pilot phase of the Village Energy Security Programme has shown several lessons and the need for improvements.
The relevance of traditional knowledge for health, well being and sustainable development - Indian Journal of Traditional Knowledge
Posted on 22 Aug, 2011 12:27 PMThis paper published in the journal Indian Journal of Traditional Knowledge is an attempt to discuss the traditional knowledge of elderly people, their role and highlights many areas w
Hydrology of the Upper Ganga river – A report by the International Water Management Institute
Posted on 21 Aug, 2011 10:43 PMTo provide the background hydrological information for the assessment of environmental flow requirements at four selected ‘Environmental Flow’ sites, a hydrological model was set up to simulate the catchment in the present state (with water regulation infrastructure) and to generate the natural flows (without water regulation infrastructure).