News and Articles
Negotiate: Reaching agreements over water - Paper by IUCN
Posted on 25 May, 2010 06:49 PM This book by IUCN is directed at practitioners involved in water-related negotiations that aim at fair and mutual agreements on optimum and sensible use of water by all. The book provides the necessary motivation, ideas, tools and inspiration for people involved in water negotiations throughout the world.
This book by IUCN is directed at practitioners involved in water-related negotiations that aim at fair and mutual agreements on optimum and sensible use of water by all. The book provides the necessary motivation, ideas, tools and inspiration for people involved in water negotiations throughout the world.
Many a times, the underlying approach to negotiations involves bargaining and competition. However, the book believes that emphasis on constructive engagement involving multiple perspectives and consensus building can lead to fair and equal distribution of this valuable resource to everyone.
The book is divided into five chapters that give out important key messages as to how to go about the process of negotiating:
Channel network delineation and catchment area demarcation of ponds: A GIS-based application
Posted on 25 May, 2010 03:06 PMContent Courtesy: GIS Development
Forwarded to the portal by: Sangeeta Deogawanka
Ponds are important sources of fresh water in the world as they store surface runoff produced by the storms. In this research paper, demarcation of the portion of land contributing runoff to ponds in village Nandgaon (Uttar Pradesh) has been done using topographical information of the surrounding area of the ponds, in a GIS interface.
Awards ceremony of the "Lost lakes of Bangalore" video contest
Posted on 25 May, 2010 01:30 PMAwards distributed to the winners of Lost lakes of Bangalore – A video contest
The awards ceremony of the Lost lakes of Bangalore video contest was held on July 3, 2010 at the TERI auditorium, Domlur.
The contest had two categories of entries – general (aimed at citizens) and the student category.
The Lost lakes of Bangalore contest elicited 23 student category and 15 general category videos, covering 32 lakes of the city.
The awards ceremony was well attended by students, participants and several citizens of Bangalore. Ms. Rohini Nilekani, Chairperson, Arghyamreinvigorated the youth to participate in redefining our lifestyles in order to reach sustainable consumption patterns.
School water, sanitation and hygiene education - Paper by Water for People
Posted on 24 May, 2010 04:52 PM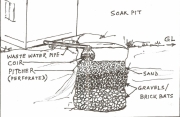 This document by Water for People, emphasises the importance of appropriate sanitation coverage in schools that is gender sensitive and culturally acceptable to the needs of both boys and girl students, rather than the exclusive focus on adequacy of facilities.
This document by Water for People, emphasises the importance of appropriate sanitation coverage in schools that is gender sensitive and culturally acceptable to the needs of both boys and girl students, rather than the exclusive focus on adequacy of facilities.
It discusses the case of schools in rural areas in West Bengal where it was found that although the coverage of sanitation facilities was reasonable, lack of adequate availability of water, lack of consideration to student differences in terms of age and gender in the construction of latrines and drinking water facilities, poor systems of maintainence and disposal of wastes made the sanitation facilities inappropriate for use.
Rank of Indian cities on sanitation (2009-10) - National Rating and Award Scheme for Sanitation in Indian Cities (MoUD)
Posted on 24 May, 2010 02:18 PMIn order to get a sense of the current status of sanitation in India's cities, a survey was initiated by the Ministry of Urban Development as a part of the National Rating and Award Scheme for Sanitation for Indian Cities. The methods used for the survey can be found on the Ministry of Urban Development website.
The findings and the rankings of the cities according to the survey found that the situation was grim with only 25 cities topping the list, while majority of the others lagged behind in terms of a number of sanitation parameters.
Holistic Engineering and Hydro-Diplomacy in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna Basin - EPW Paper
Posted on 23 May, 2010 04:49 PM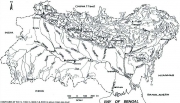 This document by Jayanta Bandyopadhyay, highlights the importance of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (GBM) basin as an important source of water for many of the countries in South Asia, and the crucial role of negotiations in the context of the impending water crisis threatening the basin with the phenomenon of climate change.
This document by Jayanta Bandyopadhyay, highlights the importance of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (GBM) basin as an important source of water for many of the countries in South Asia, and the crucial role of negotiations in the context of the impending water crisis threatening the basin with the phenomenon of climate change.
The document argues that traditional water engineering has been found to be highly reductionistic and ineffective in bringing about development in the GBM basin and the continuing poverty in the GBM basin can be linked to the absence of a holistic ecological perspective, use of an incomplete framework for economics and ignoring of long-run economic costs of the actions proposed.
Uttar Pradesh State Government invites public opinion on Groundwater Bill
Posted on 21 May, 2010 03:04 PMIn an attempt to tackle the deteriorating ground water situation in the state, the Uttar Pradesh State Government has drafted the Uttar Pradesh Groundwater Conservation, Protection and Development (Management, Control and Regulation) Bill (2010), and has invited feedback from the public.
Comments have to be sent before 5 July 2010 by email to up.gwd@rediffmail.com or by post to this address: Director, Utttar Pradesh Groundwater Department, Navam Tal, Indira Bhavan, Ashok Marg, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh.
The draft copy of the Act is uploaded on the UP State Groundwater Department website and can be downloaded here, and is also attached with this post.
Participating in Government Programmes - The Arghyam Experience (2010)
Posted on 21 May, 2010 01:25 PM Arghyam, a civil society organisation working on water issues since 2005, has participated in drinking water programmes involving State Governments since its inception, either directly or by partnering with local Civil Society Organisations (CSOs).
Arghyam, a civil society organisation working on water issues since 2005, has participated in drinking water programmes involving State Governments since its inception, either directly or by partnering with local Civil Society Organisations (CSOs).
This publication documents Arghyam's and its partners' collective experiences in participating in these Government programmes and puts forward key learnings and challenges.
The various programmes include - Sachethana, a school rooftop rainwater harvesting programme, and Suvarnajala, a flouride mitigation programme, both in Karnataka; Pani Thiye Panjo, a decentralised drinking water management programme in Gujarat; and Mazhapolima, an open-well recharge programme in Kerala.
Increasing transparency and accountability – Another win!
Posted on 14 May, 2010 11:31 AMGuest Post: Amrtha Kasturi Rangan, Arghyam
“When a State Government instead of itself undertaking a work, if it allows an agency like the petitioner Company by substantially funding them to undertake such work which is essentially that of a municipality, no one can say that such work of the petitioner company as a private activity. On the other hand, it is very much a public activity over which public interest can generate”.
Judgement in WP NO. 9794 of 2008 and M.P. Nos. 1 and 2 of 2008
The Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005 was enacted to ensure transparency and accountability. As per the Act any citizen can write and ask for information from a “public authority”. The Act also requires that public authorities make information about themselves available to the public – mandatory disclosure.
From its time of enactment, there have been several challenges in operationalizing the RTI Act. A progressive civil society has constantly challenged hesitation and delay in providing information. Several ambiguities have required judicial intervention to interpret the letter and the spirit of the Act. Here we look at the success of widening the scope of accountability to include private agencies who partner with the government under the Public Private Partnership (PPP) model.
Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bihar and mitigation strategies - A research study
Posted on 12 May, 2010 11:24 PM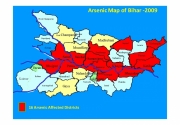 This presentation deals with the problem of arsenic contaminated aquifers in the Gangetic belt of Bihar and the failure of the state government in tackling the crisis and calls for the establishment of a centralized knowledge & research hub with an understanding of the regional peculiarities to mitigate the crisis.
This presentation deals with the problem of arsenic contaminated aquifers in the Gangetic belt of Bihar and the failure of the state government in tackling the crisis and calls for the establishment of a centralized knowledge & research hub with an understanding of the regional peculiarities to mitigate the crisis.
It traces the origin of arsenic crisis to the switch from use of surface water to groundwater. The health impacts of arsenic poisoning and the factors that aggravate arsenicosis are explained. A total of sixteen districts (fifty-seven blocks) in Bihar are affected by high levels of arsenic in groundwater, in trivalent form, which is a more toxic form of arsenic.