Rainfall and other forms of Precipitation
Groundwater assessment using remote sensing data - A case study of the Bhadra river basin - Paper presented at the National Seminar on Water and Culture (2007)
Posted on 13 Feb, 2011 11:21 PMThis method is a mathematical model, in which all the components in the water balance equation are known, and the only component which is considered unknown is the rainfall recharge.
Seasonal prediction of the Indian monsoon – An assessment using atmospheric general circulation models (AGCMs) - An article from Current Science
Posted on 13 Feb, 2011 03:57 PMThe project was a collaborative effort of the coordinators and scientists from the different modelling groups across the country. All the runs were made at the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (CDAC) at Bangalore on the PARAM Padma supercomputing system.
Prediction of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall using a state-of-the-art coupled ocean–atmosphere model - An article from Current Science
Posted on 13 Feb, 2011 03:04 PMA model of the coupled ocean–atmosphere system, the climate forecast system (CFS), from the National Centre for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), USA, has been ported onto the PARAM Padma parallel computing system at the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (CDAC), Bangalore and retrospective predictions for the summer monsoon (June–September) season of 2009 have been generated, using five initial conditions for the atmosphere and one initial condition for the ocean for May 2009.
WMO/ESCAP Panel On Tropical Cyclones - 38th session, 21st - 25th February, 2011, New Delhi
Posted on 07 Feb, 2011 12:00 PM To improve tropical cyclone warning systems in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea through effective operational plan
To improve tropical cyclone warning systems in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea through effective operational plan
Organizers: India Meteorological Department(IMD), World Meteorological Organisation(WMO), Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
Venue: Scope Complex, Lodi Road, New Delhi
Water and its quality in ancient encyclopedias of Karnataka - Paper presented at the National Seminar on Water and Culture (2007)
Posted on 30 Jan, 2011 06:40 PMThe author looks at three ancient Kannada and Sanskrit texts - Lokoparam, Manasollasa, Shivatattvaratnakara. All these texts were written between the 12th and 18th century. These texts record hydrological data ranging from cloud formation to traditional methods of preserving potable water.
Geo-hydrological studies for augmentation of spring discharge in the Western Himalaya – Final technical report by the MOWR
Posted on 23 Jan, 2011 04:39 PMIt is an attempt to understand the effect of rainfall, physiography, lithology, slope and aspect, land use practices, vegetation, altitude, soil type and anthropogenic interference (e.g., road construction and settlement etc.) and other characteristics in the spring recharge zone on the water yield and water quality of the selected springs in the mid-altitudinal belt (lesser Himalaya) in western Himalaya (Uttaranchal).
Towards adopting nanotechnology in irrigation: Micro irrigation systems
Posted on 21 Jan, 2011 07:36 PMIndia is predominantly an agricultural country and even with current orientation towards services, still agriculture contributes ¼th of total GDP of the country, 15 percent of total export and 65 % of total population’s livelihood.
Sustainable water management initiatives in Konkan under threat - A report
Posted on 21 Jan, 2011 02:09 PMGuest Post by: Parineeta Dandekar
At the first sight, Daarche Paani (‘water at the doors’) appears unreal.. on a small flat plateau called ‘Sadaa’ in konkan, an elegant cobbled walkway leads a puzzled visitor to stairs carved in stone, which go down to an ancient grove, and here is an intricate system of tanks, channels and falls which supplies water to the Panderi village and goes down as a free flowing stream, to irrigate a plantation of arecanut, pepper and mangoes in a village called Gudaghe. When I visited the place, I could see three eminent visitors, a silent lady washing her load of clothes, a fairy bluebird splashing at a tank and a huge moonmoth in one of the trees.
 Stone walkway and ancient mango trees leading to Daarche Paani.
Stone walkway and ancient mango trees leading to Daarche Paani.
Photo: Parineeta Dandekar
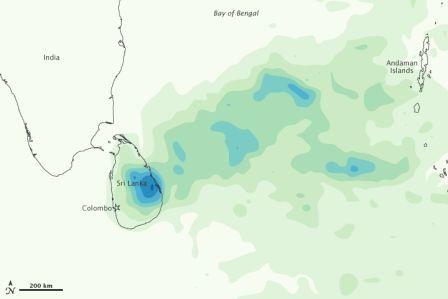
Heavy Rains in Sri Lanka - Update from Earth Observatory
Posted on 20 Jan, 2011 01:48 PMSri Lanka’s government stated that the death toll from flooding had risen to 13, and officials were arranging food drops to hardest-hit areas in the east.
![]()
India s groundwater challenges and the way forward
Posted on 18 Jan, 2011 11:42 PMIndia’s Groundwater Challenge and the Way Forward
P S Vijay Shankar , Himanshu Kulkarni , Sunderrajan Krishnan
The groundwater crisis is acquiring alarming proportions in many parts of the country. Strategies to respond to groundwater overuse and deteriorating water quality must be based on a new approach involving typologising the resource problems and redefining the institutional structure governing groundwater. This approach is based on the notion of groundwater as common property.





