Rainfall and other forms of Precipitation
Rainfall from cyclone Jal - Updates from Earth Observatory
Posted on 17 Nov, 2010 11:19 AMArticle Courtesy: Earth Observatory
Image Courtesy: NASA
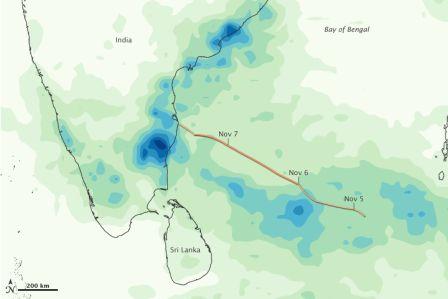 Cyclone Jal brought heavy rains to the Bay of Bengal and the southeastern coast of India in early November 2010. This color-coded map shows total rainfall over the region from November 1–7. The heaviest rainfall—more than 600 millimeters or nearly 24 inches—appears in dark blue. The lightest rainfall—less than 75 millimeters or 3 inches—appears in light green. Superimposed on the map is the storm track, with darker shades of orange corresponding with greater storm intensity.
Cyclone Jal brought heavy rains to the Bay of Bengal and the southeastern coast of India in early November 2010. This color-coded map shows total rainfall over the region from November 1–7. The heaviest rainfall—more than 600 millimeters or nearly 24 inches—appears in dark blue. The lightest rainfall—less than 75 millimeters or 3 inches—appears in light green. Superimposed on the map is the storm track, with darker shades of orange corresponding with greater storm intensity.
A band of heavy rainfall ran parallel to the November 5–7 storm track. Especially heavy rain occurred south and west of where Jal made landfall on India’s southeastern coast. The Press Trust of India attributed 11 deaths in Andhra Pradesh state to heavy rains from Jal.
Watershed development in India: Biophysical and societal impacts - Research paper from Environ Dev Sustain journal
Posted on 15 Nov, 2010 11:12 PMThe paper argues that watershed management has to be fluid to take into consideration new realities like change in flow conditions, external realities like unintended impacts and the need to maintain minimum downstream flows for environmental and other purposes.
Heavy rains, cyclones and floods affect the life of millions; News Roundup (1-7 November 2010)
Posted on 09 Nov, 2010 08:09 PMRecent news indicates extensive reports on the threat and destruction unleashed by cyclone Jal in the three states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, with the states of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka being affected the most. Cyclone Jal has led to heavy rainfall in both these states leading to floods and a heavy death toll in the coastal districts of both the states, besides reports of destruction of agricultural produce in the state of Karnataka.
South India
Andhra Pradesh
- Administration on high alert with the threat of cyclone Jal approaching the Andhra Pradesh coastline
- Cyclone 'Jal' claims lives in Andhra Pradesh
- Cyclone 'Jal' claims five lives in Andhra Pradesh
- Cyclone threat in Andhra, rains kill 20
- Andhra rains cause havoc, death toll rises to 25
- Rain claims 4 lives in Vizag, 2 in East Godavari
- Rain fury continues in Andhra Pradesh's coastal districts
- Heavy rains wreak havoc in coastal Andhra Pradesh
A case study of Dongs – The traditional water management system of the Bodo people
Posted on 05 Nov, 2010 05:24 PMThis report by SDTT presents a case study on the traditional water management system of the bodo people in Assam and North Bengal, the dongs. Dongs are man-made structures akin to canals, to route water from available water sources, which are usually perennial, to the paddy cultivating fields. The water sources are small rivers, perennial swamps, beel, streams, etc. Dong can have a breadth of 7-15 feet on average or even more. The breadth gradually increases over the course of its flow from the source till the end point.
A training manual on integrated management of watersheds by ICRISAT
Posted on 05 Nov, 2010 12:05 PMThe training manual by ICRISAT on integrated management of watersheds is meant for watershed development practitioners and provides an account of the socio-technical aspects of watershed. To begin with, the definitional aspects of watershed are spelt out -
- The term “watershed” strictly refers to the divide separating one drainage basin from another. However, over the years, the use of the term watershed to signify a drainage basin or catchment area has come to stay.
- Hydrologically, watershed could be defined as an area from which the runoff drains through a particular point in the drainage system.
Gully control in semi arid tropical watersheds – A report by ICRISAT
Posted on 04 Nov, 2010 09:21 PMThis report prepared by ICRISAT under its Global Theme on Agroecosystems deals with the problem of gully erosion, which is common in the semi-arid region, characterized by denuded landscape and flash floods. An estimated 4 million ha land in India and 29 million ha of land in Africa are affected by severe gully erosion. Gully erosion is more difficult and expensive to control than other types of soil erosion.
The Indian Summer Monsoon - Past, Present and Future - A presentation
Posted on 03 Nov, 2010 02:56 PMThe history of the United Kingdom’s interest in the Indian monsoon is discussed as also the challenges of climate change for India. Some basic facts regarding the Indian socio-economic context are presented to underline the importance of rainfed agriculture and hence the dependence on monsoons.
News roundup (22 - 31 October 2010) :" India: Land of many cell phones, but fewer toilets"
Posted on 03 Nov, 2010 08:50 AMWastewater/Sanitation
"Climate change and rainwater harvestng - Brainstorming " : Newsletter of International Rainwater Harvesting Alliance, October 2010
Posted on 28 Oct, 2010 11:31 AMNewsletter focuses on all activities concerning rainwater harvesting, the International Rainwater Harvesting Alliance (IRHA) and its partners.
A blue Pakistan, submerged, in NASA image
Posted on 27 Oct, 2010 11:09 AMNew satellite images from NASA show the extraordinary scope of the continuing disaster in Pakistan, where thousands of square miles of land remain submerged two months after the country was hit by catastrophic flooding.
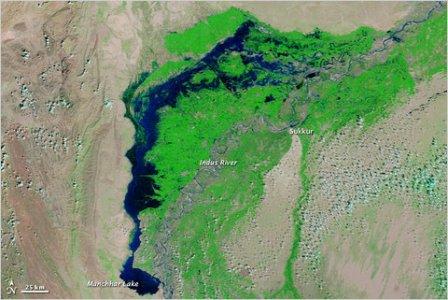 A satellite image captured last week shows flood waters lingering in Sindh Province and Manchhar Lake at twice its normal size.
A satellite image captured last week shows flood waters lingering in Sindh Province and Manchhar Lake at twice its normal size.





