Policies, Laws and Regulations
Summary report - Maharashtra government consultation on Ratnagiri and Sindhudurg districts - MoEF
Posted on 31 Jan, 2011 12:12 AMContent Courtesy: Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India
Author: Madhav Gadgil
In view of the environmental sensitivity and ecological significance of the Western Ghats region and the complex nature of its geography, as well as the possible impacts of climate change on this region, the Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India constituted a Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel to assess the current status of ecology of the Western Ghats region. The panel aimed at identifying ecologically sensitive areas in the Western Ghat region and making recommendations for the conservation, protection and rejuvenation of the region. This report presents a brief summary of the key issues that were dwelt on to understand the situation of the Western ghats and the key findings of the evaluation.
MGNREGA wage rate revision - Official notification from the MoRD
Posted on 29 Jan, 2011 10:58 AMS.O.82(E)-In exercise of the powers conferred by sub-section(1) of section 6 of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 (42 of 2005), and in supersession of the notification of the Government of India in the Ministry of Rural Development number S.O 1(E), date the 1st January, 2009, except as respects things done or omitted to be done before such supersession, the Central Government hereby specifies the wage rate payable to the unskilled manual worker under column (3) in respect of the state or the Union Territory mentioned in column (2) of the Schedule given below, working on various schemes under the said Act, with from the 1st day of January, 2011
Draft strategic plan 2010-2022, for rural drinking water
Posted on 28 Jan, 2011 03:49 PMForwarded to the portal by: Sujoy Majumdar, DDWS through the
Whose water? Privatisation of water, a bane for consumers
Posted on 18 Jan, 2011 11:47 PMAll of us have felt the joy of slaking one's thirst with water, washing away the unforgiving heat of a Delhi summer with a cool glass of water. But have you ever paused to think about where we get our water from? How are we using this resource? Is it finite or will be always get clean water, everyday, for all our needs?
Campaign against pollution of the Aril river in Moradabad district, U.P
Posted on 18 Jan, 2011 11:45 PMThis pollution has been caused by a paper factory that was set up 16 years ago. The noise, air, land and water pollution that are a direct result of the factory have changed a beautiful and peaceful rural area into one where farmers’ land and crops have been destroyed, the air is full of fine, crystalline ash, the local river is an evil-smelling, stagnant mire of foam-encrusted sludge and the water table has fallen by over 70 feet.
Eastern Himalaya freshwater biodiversity assessment report released by IUCN and Zoo Outreach Organisation
Posted on 18 Jan, 2011 11:44 PMDear all,
IUCN, with Zoo Outreach Organisation, have today published a new report, 'The status and distribution of freshwater biodiversity in the Eastern Himalaya', which is available online here
The report of the Krishna Water Disputes Tribunal-II (2010)
Posted on 18 Jan, 2011 08:26 PM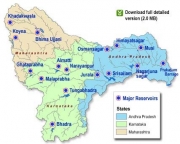 KWDT-II freshly assessed the yearly yields in the Krishna and determined the award on the basis of the yearly yield at 65 per cent dependability which was assessed at a total of 2,293 tmcft.
KWDT-II freshly assessed the yearly yields in the Krishna and determined the award on the basis of the yearly yield at 65 per cent dependability which was assessed at a total of 2,293 tmcft.
In its order, announced in an open court, the tribunal allocated a total share of 1,001 tmcft to Andhra Pradesh, 911 tmcft to Karnataka and 666 tmcft to Maharashtra with certain restrictions imposed on each State in keeping with the dependable flows of the rivers on which the allocations have been made. The allocation under the first award (KWDT I) was 811 tmcft for Andhra Pradesh, 734 tmcft for Karnataka and 585 tmcft for Maharashtra.
Maharashtra Groundwater (Development and Management) Bill (2009)
Posted on 05 Jan, 2011 07:32 PMThe Maharashtra Groundwater (Development and Management) Bill, 2009 aims to facilitate and ensure sustainable and adequate supply of groundwater of prescribed quality, for various category of users, through supply and demand management measures, protecting public drinking water sources and to establish the State Groundwater Authority and District Level Authorities to manage and to regulate, with community participation, the exploitation of groundwater within the State of Maharashtra.
Climate change: Vulnerability and adaptation experiences from Rajasthan and Andhra Pradesh – A report by SDC
Posted on 05 Jan, 2011 06:44 PM This document discusses the process oriented programme of Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) on Vulnerability Assessment (V&A) and Enhancing Adaptive Capacity to Climate Change initiated in the semi-arid regions of India. The aims of this programme include strengthening the resilience of local communities to conditions of unfavourable weather, like adverse alterations in temperature and precipitation leading to the more frequent occurrence of drought and to use the experiences for policy development for climate change adaptation measures at various levels.
This document discusses the process oriented programme of Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) on Vulnerability Assessment (V&A) and Enhancing Adaptive Capacity to Climate Change initiated in the semi-arid regions of India. The aims of this programme include strengthening the resilience of local communities to conditions of unfavourable weather, like adverse alterations in temperature and precipitation leading to the more frequent occurrence of drought and to use the experiences for policy development for climate change adaptation measures at various levels.
Over 60 per cent of the cultivated area in India is rainfed & unfavorable and uncertain rainfall patterns will seriously affect the food, drinking water and livelihood security of millions of children, women and men. Since the initiation of this project, the emphasis on proactive research on adaptation mechanisms has increased at the national level.
The present decade may mark the beginning of a new climate era, characterized by extreme and often unpredictable weather conditions and rise in sea levels. The greatest casualty of climate change will be food, water and livelihood security.
Damming North East India - Juggernaut of hydropower projects threatens social and environmental security of region
Posted on 28 Dec, 2010 07:49 PM This report by Kalpavriksh, Aaranyak and ActionAid India deals with the large dams’ juggernaut, which happens to be the biggest ‘development’ intervention in this ecologically and geologically fragile, seismically active and culturally sensitive region in the coming days. With the Northeast identified as India’s ‘future powerhouse’ and at least 168 large hydroelectric projects set to majorly alter the riverscape, large dams are emerging as a major issue of conflict in the region.
This report by Kalpavriksh, Aaranyak and ActionAid India deals with the large dams’ juggernaut, which happens to be the biggest ‘development’ intervention in this ecologically and geologically fragile, seismically active and culturally sensitive region in the coming days. With the Northeast identified as India’s ‘future powerhouse’ and at least 168 large hydroelectric projects set to majorly alter the riverscape, large dams are emerging as a major issue of conflict in the region.
Although the current scale of dam-related developments far outstrips anything which took place in the past, the region has been no stranger to dam-related conflicts. For example, the Kaptai dam, built in the Chittagong Hill Tracts of East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) in the 1960s, submerged the traditional homelands of the Hajong and Chakma indigenous communities, and forced them to migrate into parts of Northeast India.