Surface Water
"In Search of Yamuna: Reflections on a River Lost" - A recent book as an ode to rivers
Posted on 27 Apr, 2011 02:26 PMAbout the book
 In the present mood of transience and conflict, amidst the emerging riverfront politics, these communities seem to be caught in the eye of the storm.
In the present mood of transience and conflict, amidst the emerging riverfront politics, these communities seem to be caught in the eye of the storm.
Dwarekeshwar river basin of West Bengal : A unique combination of flash flood zone, monsoonal flood zone & tidal zone
Posted on 27 Apr, 2011 12:59 PM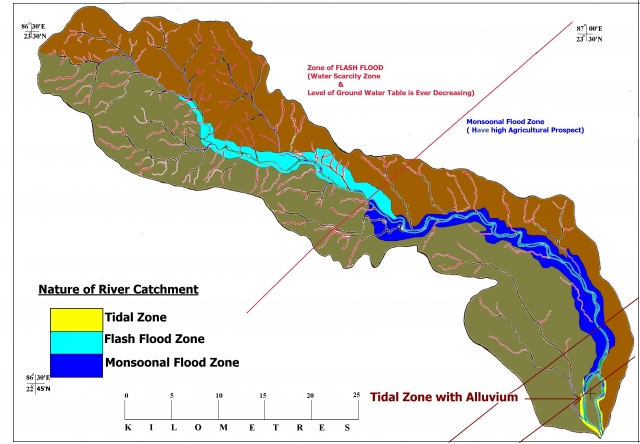 In India, at national level when all the planners are saying about the water grid, river linking project, i
In India, at national level when all the planners are saying about the water grid, river linking project, i
Citizen's uprising against encroachment and pollution of Ram Nadi, an urban river in Pune, Maharashtra
Posted on 25 Apr, 2011 11:37 AMForwarded to the portal by: Parineeta Dandekar
History of irrigation in Bihar – Ancient, British and upto Pre-plan Period – A report by the Water and Land Management Institute, Patna
Posted on 23 Apr, 2011 10:29 AMIrrigation is being practiced there since ancient times dating back to Kautilya, who lived in Patliputra (now Patna), which was the capital of the mighty Mauryan empire (400 BC). Kautilya had laid down the principles on rainfall and irrigation in his famous book Kautilya Arthasashtra.
Inviting endorsements on a submission to the WGEEP for declaring the rivers in the Western Ghats as Ecologically Sensitive Areas (ESAs)
Posted on 22 Apr, 2011 12:58 PMDear friends,
We are all aware of the immense ecological, cultural and social significance of rivers originating and flowing through the Western Ghats. This includes source regions of East flowing rivers like Krishna, Godavari and Cauvery and the source, riparian and estuarine region of all West flowing rivers.
We are lucky to still have some of the very few and very rare 'free flowing rivers' in the country. Most of the rivers in our country have been dammed and diverted. This has changed the ecological and physical characteristics of these rivers completely. Today, it is difficult for us to visualise the amazing range of ecological goods and services that an undammed, free flowing river can provide. Some such rivers in the Western Ghats are Shastri, Aghanashini, Gargai and Seetha Nadi.
Groundwater: From mystery to management - An article by TN Narasimhan
Posted on 22 Apr, 2011 12:07 PMGroundwater has been used for domestic and irrigation needs from time immemorial. It is a component of the hydrological cycle, vital for human sustenance. Unlike surface water, groundwater cannot be readily observed. Consequently, it was long considered to be mysterious or even occult in nature, influencing legal decisions relating to groundwater ownership and use.
Proposal for groundwater recharge in National Capital Region - A report by SK Sharma and Green Systems
Posted on 22 Apr, 2011 11:53 AMIt also explains the various laws that have been put in place to increase groundwater replenishment.
Development of training module for water safety plan in urban areas - A document by ESCI
Posted on 20 Apr, 2011 03:48 AMA Water Safety Plan (WSP) is an improved risk management tool designed to ensure the delivery of safe drinking water. It identifies hazards, means to control them, means and actions to identify loss of control and its restoration. It comprises system assessment and design, operational monitoring and management plans (including documentation and communication). Water quality guidelines have been issued by the WHO.
Drinking water quality monitoring and development of surveillance mechanisms - A pilot study done by NEERI in New Delhi
Posted on 20 Apr, 2011 02:30 AMThe WHO guidelines for drinking water quality aim to protect public health and the key way to ensure this is through the adoption of Water Safety Plans (WSP). WSP includes setting of health targets, risk analysis and its assessment to identify priority hazardous scenarios and management of the risk.
Guidelines for water safety plans for rural water supply systems - A document by SIAES and WHO India (2009)
Posted on 20 Apr, 2011 01:10 AM Delivery of safe drinking water is vital for protecting public health and of promoting more secure livelihoods.
Delivery of safe drinking water is vital for protecting public health and of promoting more secure livelihoods.
The traditional approach to water quality and safety management has relied on the testing of drinking water, as it leaves the treatment works or at selected points, either within the distribution system or at consumer taps. It is referred to as ‘end‐product testing’.





