Rainfed Agriculture
Saving some last remaining free flowing rivers
Posted on 24 Jan, 2012 06:38 AMGuest post by: Parineeta Dandekar
Changing currents: Plumbing the rights: A film highlighting water as a common good
Posted on 10 Jan, 2012 08:55 PMSource: Culture Unplugged
Democratisation of water management - The experience of Tamil Nadu with governance reforms
Posted on 09 Jan, 2012 12:18 PMNor is the introduction of the private sector and the reduction in the role of the government going to help. Rather, the time has come to introduce changes at the basic or the fundamental level in the way in which the water sector functions.
There is an urgent need to bring about reforms in governance by moving towards decentralisation and democratisation, leading to involvement of people from all the sections of the society, who know and understand that they are responsible for the system and its functioning, as well as by introducing principles of equity and social justice. The papers demonstrate the successful implementation of this approach by describing the experience of Tamil Nadu at democratising water management through introduction of reforms at the level of governance, through involvement of the Tamil Nadu Water Supply and Drainage Board (TWAD).
A survey of point of use household water treatment options for rural south India: A report detailing resources available
Posted on 07 Jan, 2012 10:59 AMPoint of use household water treatment is the process of treating water at the household level to improve its microbiological purity. In cases where treated municipal water is not available, or is subject to recontamination due to a faulty distribution system, household water treatment is essential and allows families control over their drinking water.
Living rivers, dying rivers: Bagmati river in Nepal
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 06:07 PMBagmati river in Kathmandu: From holy river to unthinkable flowing filth
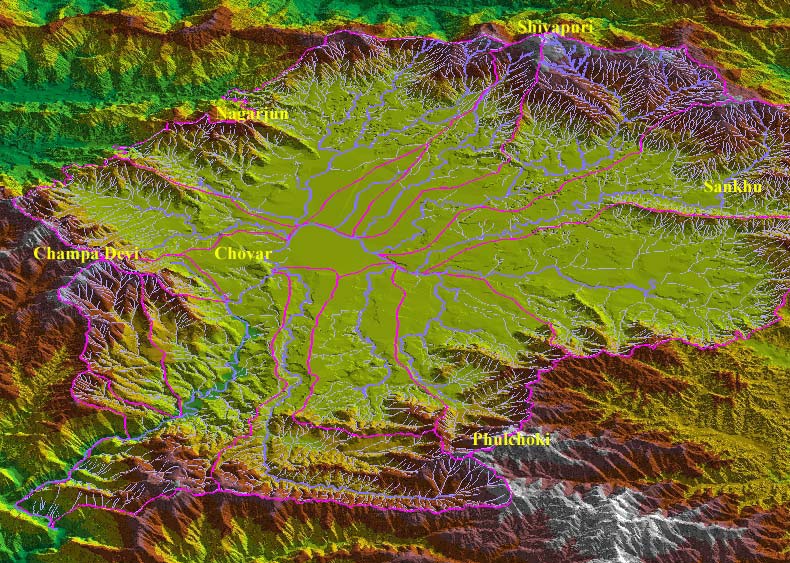
Ajaya Dixit initiated his presentation with a general account of how rivers shape the landscape and how riverine ecosystems have nurtured society and kept civilisations vibrant, cultured and creative. Dixit went on to discuss the basin characteristics of the Bagmati, a tributary of the Kosi that rises in the Shivapuri hills, north of the Kathmandu valley. Around fifteen percent of the basin area (3700 sqkm) lies in Nepal, while the remaining is in India. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1400 mm and is more than 2000 mm in the hills. Bagmati is a seasonal river with rainfall and springs as its main source. Its mean flow is 15.6 cubic metre/second and low flow is 0.15 cubic metre/second in April.
Kathmandu lies in the Upper Bagmati basin and studies suggest that an ancient lake called the Paleo-Kathmandu lay within the Kathmandu valley as a lacustrine formation. Early settlers lived in lower slopes and used springs and river in the upper reaches. When they moved to the valley floor, they built dongia dharas, which are stone water spouts fed by the unconfined aquifers and delivered water through surface channels. Even today, dongia dharas dated back to 1500 years exist. The state built canals (raj kulo) tapped the upper stretches of the rivers close to the mountains. Rivers and irrigation helped recharge aquifers and ponds.
However, rising urbanisation has damaged these ancient artifacts. Over the last sixty years Kathmandu has expanded massively and its population has increased from 0.41 million in 1951 to 2.6 million in 2011. The city has a huge transient population aside from this, reducing it to a concrete nightmare. Seismologists suggest that Kathmandu is a rubble city in the making. Though the Bagmati river flow has not changed significantly in the last seventy years, the character of the river has been transformed significantly during the period 1970 to 1990. The river has been canalised while the dumping of the city’s garbage into it continues. Dixit identified a plethora of problems faced by the river such as upstream water diversion for drinking water needs, disposal of untreated liquid waste, disposal of solid waste, river jacketing for roads and commercial activities, sand mining and physical encroachment.
The state of the river is an outcome of the current approach to waste management particularly liquid waste management. Three types of waste water namely yellow water flux, grey water and yellow black flux are being generated and flowing water is being used as a vehicle to dispose these. The idea of a water based disposal system e.g. flush toilet embedded in Victorian engineering has led to a technological lock-in with the result that the notion of a natural hydrological cycle has undergone a fundamental transformation.
All the same, the bulk of the load in the river is biological though there are some factories releasing effluents. In the last 20 years some of them have been closed or relocated and the river now stands a chance of being salvaged.

Managing natural resources through simple and appropriate technological interventions for sustainable mountain development - Current Science (2011)
Posted on 30 Dec, 2011 10:07 AMThe initiative on management of natural resources through appropriate interventions aimed at:
Agriculture, food security and nutrition in Vidarbha: Household level analysis – A special article in EPW
Posted on 27 Dec, 2011 09:43 AMUsing the data generated from a baseline survey on a sample of 6,990 households covering six districts, this paper attempts to assess the relationships between agriculture, food security and nutrition for children, adolescents and married women of reproductive age.
BDWS invites applications for Project Manager IRRAS, Bihar – Apply by December 23, 2011
Posted on 17 Dec, 2011 09:12 AMContent courtesy: DevNetJobsIndia
![]()
Bihar Water Development Society (BDWS) works on projects related to education, health care, self-help groups and socio-economic development programmes. The basic purpose behind these activities is to work for the upliftment of the rural masses and to alleviate the sufferings of the poor, the marginalized, especially of women who are deprived of self-dignity, confidence and self-respect and handicapped in many ways while struggling to come to the main stream of society.
Strengthening rural livelihoods – A report by IDRC
Posted on 13 Dec, 2011 05:17 PM This report prepared by International Development Research Centre (IDRC) examines how information related constraints in poor rural areas are being overcome and how information technology is being employed to the benefit of people in South Asia.
This report prepared by International Development Research Centre (IDRC) examines how information related constraints in poor rural areas are being overcome and how information technology is being employed to the benefit of people in South Asia.
Poor people are constrained by limited access to information and poor communications technology. The research looked at the use of ‘information communications technologies’ (ICTs) in providing agricultural extension services, getting timely market price information, finding out about rural wage labour opportunities, helping rural communities to build a sustainable asset base and understanding crop diseases and soil nutrition.
The results of the research bring together rigorously tested practices and methods of applying ICTs for improving rural livelihoods. Each research study has investigated how and to what extent a specific ICT intervention made a difference. Together it shows how ICTs have empowered rural people and transformed livelihoods in agriculture: by filling information gaps, raising awareness, building skills and extending social networks.
The focus was on agricultural communities, as Asia’s poor and middle-income countries have primarily agriculture-based economies. However, a broader ‘livelihoods’ approach has been taken to ensure that we observe the variety of ways ICTs can have an effect on rural communities. The scope of the research took into account the range of on-farm and off-farm productive and reproductive activities that support farming households and communities.
Performance audit of food security schemes in Orissa and Uttar Pradesh – A report by Centre for Environment and Food Security
Posted on 13 Dec, 2011 04:55 PMThe schemes covered under this audit include, (a) Public Distribution System (PDS), (b) Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY), (c) Mid-day Meals (MDM), (d) Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), (e) National Old Age Pension Scheme (NOAPS), (f) National Family Benefit Scheme (NFBS), (g) Annapurna, (h) National Maternity Benefit Scheme (NMBS), (i) Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY), and (j) National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS).




