Groundwater
Challenges of sustainable water quality management in rural India - Current Science
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 04:51 PM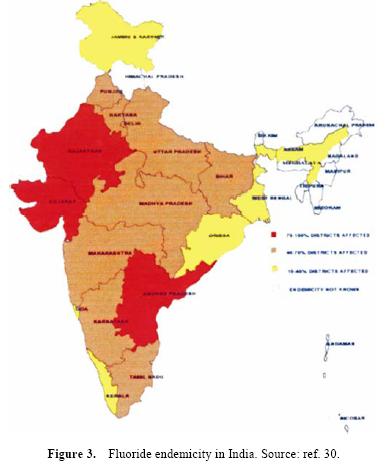 The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
While access to drinking water in India has increased over the past decade, the tremendous adverse impact of unsafe water on health continues. It is estimated that about 21% of communicable diseases in India are water related.
Although some degree of intervention in terms of chlorination and monitoring of water quality exists in major cities and towns, rural India, which constitutes the bulk (70%) of the population, is usually deprived of such interventions. The population in rural India is mainly dependent on the groundwater as a source of drinking water. As a quality concern the groundwater is often found to be contaminated with fluoride, arsenic, iron and salts. In recent years, fluorosis has emerged as major public health issue in rural India.
Sanitation - The hygienic means of promoting health - Indian Journal of Public Health
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 11:10 AMThis article published in the Indian Journal of Public Health highlights the importance of sanitation as hygienic means of dealing with health of populations and presents the history and the definition of sanitation and highlights t
Virological evaluation of domestic water purification devices in India - Inadequate quality and the need for virological standards - Tropical Medicine and International Health
Posted on 14 Aug, 2011 03:36 PMThis paper published in the journal
The challenges of ecological sanitation in coastal south India - A case study of Kovalam town - South Chennai (Tamil Nadu) - A presentation
Posted on 11 Aug, 2011 05:48 PMThis presentation by Sekhar Raghavan, Director, Rain Centre, Chennai, India highlights the experiences and the challenges faced by Rain Centre in introducing ecological sanitation in the coastal town of Kovalam near Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India along with Coastal and Rural development Trust (CRDT), a small non profit centre based in Kovalam .
The coastal town of Kovalam was selected as a case because of its peculiar situation with its location in a fast developing peri-urban area in proximity to Chennai city characterised by good groundwater situation, adequate land and housing facilities, but with a glaring and urgent need and demand for toilets.
Dynamic groundwater resources of Maharashtra – A report by CGWB and GSDA (2004)
Posted on 08 Aug, 2011 04:35 PMThis report on “Dynamic Ground Water Resources of Maharashtra (2004)” presents the groundwater estimates for the State of Maharashtra as computed by the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) and Groundwater Survey and Development Agency (GSDA) based on the guidelines given by the Groundwater Estimation Committee (GEC-1997) constituted by Ministry of Water Resources (Government of India).
Urbanization and intersectoral competition for water – A report by Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars
Posted on 07 Aug, 2011 07:24 PMThe report by Paul P Appasamy and Ruth Meinzen Dick deals with urbanization and intersectoral competition for water founded on the view that stereotypical images of “thirsty cities” that equate urban demand with “drinking water” or factories, and rural water supply with irrigation do not adequately portray the water uses in each area.
Delhi Water Privatization - WASH News and policy update
Posted on 03 Aug, 2011 06:20 PMContent courtesy: India WASH Forum
Sustainable Development Framework for the mining sector in India – A report by the Ministry of Mines
Posted on 29 Jul, 2011 01:03 PM It does this in light of the recommendations of the Anwarul Hoda Committee, a High Level Committee set up by the Planning Commission in 2005. The draft SDF prepared by ERM India Pvt. Ltd. for the Ministry of Mines was released recently for seeking public comments before its formal adoption. It presents a set of guiding principles for the mining sector in India, which aims at achieving resource efficiency, business viability and environment stewardship around development of affected communities.
It does this in light of the recommendations of the Anwarul Hoda Committee, a High Level Committee set up by the Planning Commission in 2005. The draft SDF prepared by ERM India Pvt. Ltd. for the Ministry of Mines was released recently for seeking public comments before its formal adoption. It presents a set of guiding principles for the mining sector in India, which aims at achieving resource efficiency, business viability and environment stewardship around development of affected communities.
The political economy of sanitation - How can we increase investment and improve service for the poor? – A report by Water and Sanitation Program
Posted on 26 Jul, 2011 02:53 PM This global study attempts systematically to understand and thus help practitioners manage the political economy of pro-poor sanitation investments and service provision.
This global study attempts systematically to understand and thus help practitioners manage the political economy of pro-poor sanitation investments and service provision.
It aims to provide practical advice to multi-lateral agencies and sanitation practitioners to help them better manage stakeholder relations and effectively maneuver within the complex institutional relationships of the sanitation sector in order to enhance the design, implementation, and effectiveness of operations that provide pro-poor sanitation investments and services. The ultimate goal is to improve health and hygiene outcomes.
This study follows current approaches to political economy - interdisciplinary inquiry drawing upon social and political theory and economic principles - to understand how political actors, institutions, and economic processes influence each other. This study’s conceptual framework combines a diagnostic component with a typology of actions to help translate analytical findings into more effective support to operations and investments.
Kailash sacred landscape conservation initiative - Feasibility assessment report by ICIMOD
Posted on 25 Jul, 2011 03:19 PM This publication by International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) deals with Kailash Sacred Landscape Conservation Initiative (KSLCI), a project that seeks to conserve and sustainably manage a highly unique and special landscape through the application of trans-boundary ecosystem management approaches.
This publication by International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) deals with Kailash Sacred Landscape Conservation Initiative (KSLCI), a project that seeks to conserve and sustainably manage a highly unique and special landscape through the application of trans-boundary ecosystem management approaches.
This region, like much of the rest of the Hindu Kush-Himalayas, faces many challenges, not the least of which are global warming, globalisation and environmental degradation. The Kailash region is considered sacred to five major religions and to a large number of people in Asia and throughout the world. This area is historically, ecologically, and culturally interconnected and is the source of four of Asia’s most important rivers.
The KSLCI is an attempt on the part of the three neighbouring countries of India, China and Nepal to join hands to help preserve the unique biological diversity, the many ecosystem goods and services, and the value-based cultural heritage of one of the most revered and sacred landscapes in the world.




