Contamination, Pollution and Quality
Community managed sanitation in Kerala - Tools to promote governance and improve health - A Report by the World Bank Institute
Posted on 16 Jan, 2012 01:14 PMIt also deals with the efforts made by the Government of India to revolutionise sanitation services in the state of Kerala, with the aim of improving public health. Earlier experience had shown that significant governance problems had hindered water and sanitation reforms in local and national programmes in the state.
The unquiet river: An overview of select decisions of the courts on the river Yamuna
Posted on 14 Jan, 2012 06:40 PMThe river has attained the distinction of being perhaps the river attracting the most judicial attention in india, after the Ganga. This report analyses the various laws and judicial decisions pertaining to the Yamuna and their effects on the river.
Environment Statistics – A compendium by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (2011)
Posted on 07 Jan, 2012 04:25 PMIt broadly covers five core parameters, viz., biodiversity, atmosphere, land/soil, water and human settlements suggested by the Framework for Development of Environment Statistics (FDES) published by United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) in 1984.
Surveillance of drinking water quality - safe water Initiative - A presentation
Posted on 07 Jan, 2012 10:28 AMThis presentation by Dr.Nanoti at the 'International Conference on Health and Environment' organised by Centre for Science and Environment explains the method and importance of regular monitoring of drinking water quality in urban areas.
The presentation begins with the argument that managers of urban water supply systems stand to benefit from the fresh perspective offered by an external assessor.
Norms and standards of municipal basic services in India: Report by the National Institute of Urban Affairs
Posted on 07 Jan, 2012 10:04 AMStudies indicate that the levels of infrastructure services available in urban regions in India are improving, however their quality is still debatable. This paper uses secondary data available from various government report to review the norms and standards for the following basic services
- Water supply
- Sewereage
- Solid waste management
- Primary education
- Preventive health care
In addition resource gaps and measures to bridge these gaps are also examined.
Sustainable groundwater management – Report of the Working Group of the Planning Commission for the 12th Five Year Plan
Posted on 06 Jan, 2012 04:27 PMThe existing methodology of groundwater resources assessment is appropriate and suitable for country-wide groundwater resources estimation, considering the present status of database available with the Central and State agencies.
Living rivers, dying rivers: Bagmati river in Nepal
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 06:07 PMBagmati river in Kathmandu: From holy river to unthinkable flowing filth
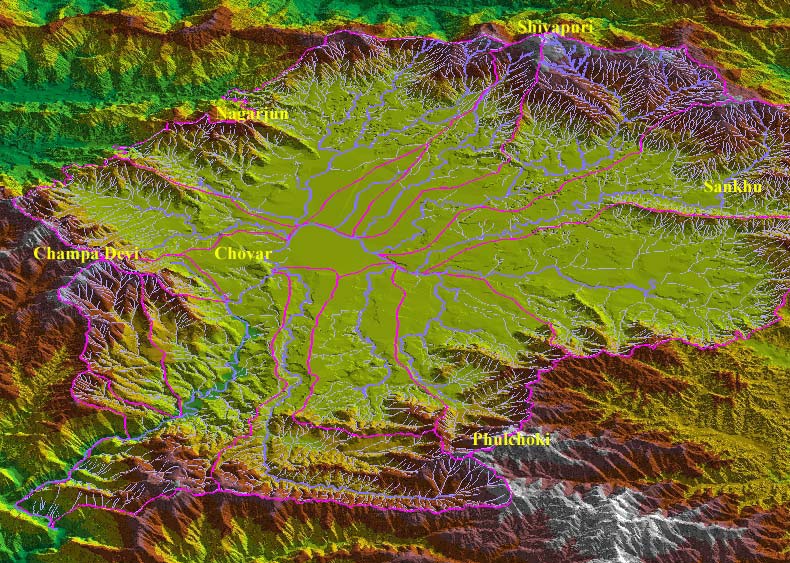
Ajaya Dixit initiated his presentation with a general account of how rivers shape the landscape and how riverine ecosystems have nurtured society and kept civilisations vibrant, cultured and creative. Dixit went on to discuss the basin characteristics of the Bagmati, a tributary of the Kosi that rises in the Shivapuri hills, north of the Kathmandu valley. Around fifteen percent of the basin area (3700 sqkm) lies in Nepal, while the remaining is in India. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1400 mm and is more than 2000 mm in the hills. Bagmati is a seasonal river with rainfall and springs as its main source. Its mean flow is 15.6 cubic metre/second and low flow is 0.15 cubic metre/second in April.
Kathmandu lies in the Upper Bagmati basin and studies suggest that an ancient lake called the Paleo-Kathmandu lay within the Kathmandu valley as a lacustrine formation. Early settlers lived in lower slopes and used springs and river in the upper reaches. When they moved to the valley floor, they built dongia dharas, which are stone water spouts fed by the unconfined aquifers and delivered water through surface channels. Even today, dongia dharas dated back to 1500 years exist. The state built canals (raj kulo) tapped the upper stretches of the rivers close to the mountains. Rivers and irrigation helped recharge aquifers and ponds.
However, rising urbanisation has damaged these ancient artifacts. Over the last sixty years Kathmandu has expanded massively and its population has increased from 0.41 million in 1951 to 2.6 million in 2011. The city has a huge transient population aside from this, reducing it to a concrete nightmare. Seismologists suggest that Kathmandu is a rubble city in the making. Though the Bagmati river flow has not changed significantly in the last seventy years, the character of the river has been transformed significantly during the period 1970 to 1990. The river has been canalised while the dumping of the city’s garbage into it continues. Dixit identified a plethora of problems faced by the river such as upstream water diversion for drinking water needs, disposal of untreated liquid waste, disposal of solid waste, river jacketing for roads and commercial activities, sand mining and physical encroachment.
The state of the river is an outcome of the current approach to waste management particularly liquid waste management. Three types of waste water namely yellow water flux, grey water and yellow black flux are being generated and flowing water is being used as a vehicle to dispose these. The idea of a water based disposal system e.g. flush toilet embedded in Victorian engineering has led to a technological lock-in with the result that the notion of a natural hydrological cycle has undergone a fundamental transformation.
All the same, the bulk of the load in the river is biological though there are some factories releasing effluents. In the last 20 years some of them have been closed or relocated and the river now stands a chance of being salvaged.

SWSM invites applications for State Consultant – Water Quality, Ranchi, Jharkhand – Apply by January 5, 2012
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 08:59 AMContent courtesy: DevNetJobsIndia


Description:
The flagship programmes of Government of India, Total Sanitation Campaign (TSC) and National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP) are being implemented by the State Water and Sanitation Mission (SWSM) Jharkhand, Government of Jharkhand. The NRDWP guideline makes provision for a state level Water and Sanitation Support Organisation for taking up various support activities under the drinking water and sanitation sector. In Jharkhand the state level Programme Management Unit, which is registered as a society has been working on planning, monitoring and support in programme implementation. The State Water and Sanitation Mission, Jharkhand wishes to recruit a State Co-ordinator (Water Quality).
Performance audit of water pollution in India – A report by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India
Posted on 03 Jan, 2012 11:44 AM The issue was examined by CAG because various stakeholders working in the field of environment flagged water pollution as the most important environmental issue that concerns us.
The issue was examined by CAG because various stakeholders working in the field of environment flagged water pollution as the most important environmental issue that concerns us.
The audit was conducted through document analysis, collection of responses to questionnaires, physical collection and testing of samples. The results of audit, both at the Central level and the State level, were taken into account for arriving at audit conclusions.
First international advocacy planning meeting for water and sanitation activists'- 'WASH News and policy update
Posted on 30 Dec, 2011 12:31 PMContent courtesy: India WASH Forum