Rivers
Basin maps of Indus river showing basin indicators, landcover classes and biodiversity information and indicators
Posted on 17 Apr, 2009 01:05 PM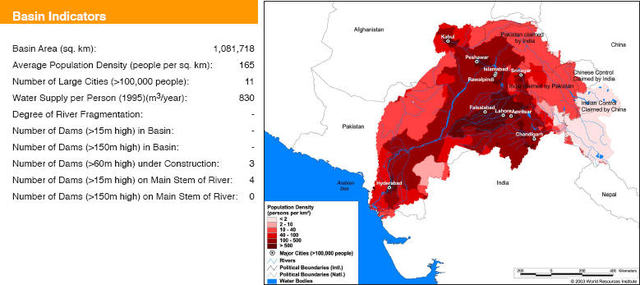
Basin maps of Narmada river showing basin indicators, landcover classes and biodiversity information and indicators
Posted on 17 Apr, 2009 12:55 PM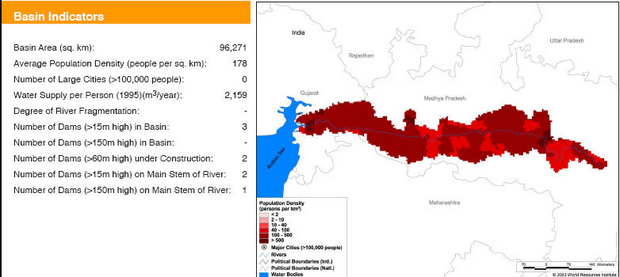
Basin indicators map of Narmada river basin
Basin maps of Godavari river showing basin indicators, landcover classes and biodiversity information and indicators
Posted on 17 Apr, 2009 12:42 PM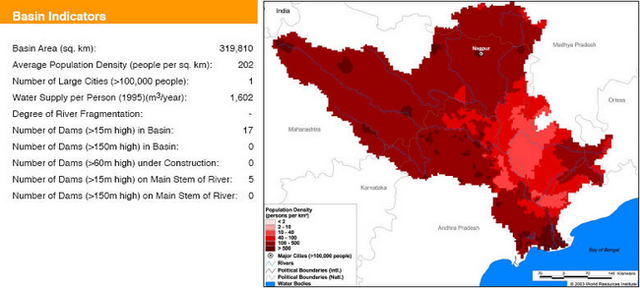
Basin indicators map of Godavari river basin
Basin maps of Ganga river showing basin indicators, landcover classes and biodiversity information and indicators
Posted on 17 Apr, 2009 11:08 AMGanga river basin
Basin maps of Tapti river showing basin indicators, landcover classes and biodiversity information and indicators
Posted on 17 Apr, 2009 10:37 AM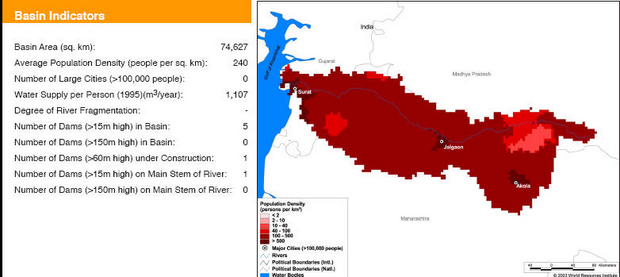
Basin indicators map of Tapti river basin
Compilation of data for Cauvery basin for river basin planning along with maps of major river basins of India
Posted on 17 Apr, 2009 09:49 AMWater flows without regard to political and administrative boundaries. Water planning with respect to rivers should therefore be done for the river basin (or sub-basin) as a whole. River basin planning also has to look in an integrated way at all the relevant parameters like urban and rural populations, water usage patterns, water pollution, wastewater flows.
Cauvery basin: its culture, places of historical significance, birth place, climate, precipitation, catchment, tributaries, state-wise spread, landuse
Posted on 14 Apr, 2009 12:21 PMCulture and places of historical significance
The river Cauvery has been the inspiration for various civilizations who have thrived on the banks of the river. This can be seen manifested in the various forms of art, culture and philosophy that have originated along the course of the river.
Kosi Katha - The making of a famine': Video highlighting the growing famine in the wake of the floods in Bihar
Posted on 14 Apr, 2009 04:05 AM
The latest loss figures (24 Feb. 09 is five districts, 35 blocks, 33.29 lakh peopla, 9.97 lakh live stock., affected area 3.68 lakh hectares, 2.37 lakh houses, 527 human death a and 19,323 loss of cattle.
Hydroelectric power projects & climate change: A case study of Ravi basin in Himachal Pradesh
Posted on 09 Apr, 2009 11:34 AMThe following is a paper by Dr. Mohinder Slariya based on data collected during his Ph.D work. The work contains data sourced from the India Water Portal, and aims to illustrate local area climate changes with the development of hydroelectric projects. The abstract of the paper has been quoted below, with the full paper available as a download!
Abstract
Dams have had serious impacts on the lives, livelihoods, cultures and spiritual existence of indigenous, tribal and illiterate people, moreover on the physical environmental conditions and on the biodiversity of the area concerned. The dam related developmental activities in Ravi catchment area have been threatening the biodiversity in the whole catchment. There are more than 50 rivulets in the Ravi catchment and on which more than 70 power projects have been planned by the government by putting biodiversity at the stake. Developmental activities have unintentionally produce weather and climate modifications on a larger scale and threaten the existing biodiversity. Such developmental activities have been started day back in 1980s in Ravi basin with the installation of Baira Suil Power Project and today it has covered all most all Ravi basin starting from interstate broader of Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab and Himachal Pradesh and engulfed the green cover of the area. Because of this extinction the catchments area is experiencing drastic climatic changes, because of 100 km reservoirs of Shahpur Kandi (125MW), Thein Dam (600MW), Chamera-I (540MW) and Chamera-II (300 MW) and tunnelization of Ravi in 19.38 kms with a dia of 7 to 9 meters and 102 meters high surge shafts with 15.5 meters dia and underground power houses of Chamera-I & II and dry Ravi in almost all its natural route (27 kilometers in Chamera I & II). In this dry region there is a tremendous increase in the temperature and there is no timely and usual rain in the basin after the installation of power projects.
Kosi darshan: A deeper look at the lives of those pinned on the river
Posted on 31 Mar, 2009 05:14 PM"If it had not breached at Kusaha, it would have anyway breached at this point," points a villager towards the probable location on the eastern bank in village Rajabaas near Prakashpur in Sunsari district of Nepal, located 14 km upstream of Kusaha where the Eastern Afflux embankment of the Kosi had breached on the August 18, 2008.