Wells and Step-wells
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) on Groundwater - Understanding the basics
Posted on 08 Sep, 2011 04:56 PMA comprehensive FAQ Manual on Groundwater authored by Dr Mihir Kumar Maitra narrows down the existing knowledge gaps amongst the common groundwater users.
The most popular FAQs are listed below. Please click on a topic to view more detailed information:
Basic information on groundwater

Groundwater, self-supply and poor urban dwellers - A review with case studies of Bangalore and Lusaka by IIED
Posted on 24 Aug, 2011 08:32 PMIt investigates the difficulties they face and emphasizes the need for better integration of groundwater in the planning and management of urban water resources.
Challenges of sustainable water quality management in rural India - Current Science
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 04:51 PM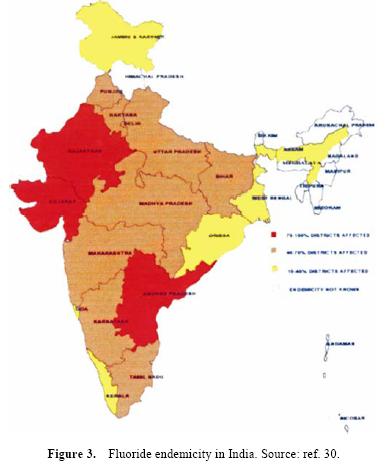 The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
While access to drinking water in India has increased over the past decade, the tremendous adverse impact of unsafe water on health continues. It is estimated that about 21% of communicable diseases in India are water related.
Although some degree of intervention in terms of chlorination and monitoring of water quality exists in major cities and towns, rural India, which constitutes the bulk (70%) of the population, is usually deprived of such interventions. The population in rural India is mainly dependent on the groundwater as a source of drinking water. As a quality concern the groundwater is often found to be contaminated with fluoride, arsenic, iron and salts. In recent years, fluorosis has emerged as major public health issue in rural India.
Dynamic groundwater resources of Maharashtra – A report by CGWB and GSDA (2004)
Posted on 08 Aug, 2011 04:35 PMThis report on “Dynamic Ground Water Resources of Maharashtra (2004)” presents the groundwater estimates for the State of Maharashtra as computed by the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) and Groundwater Survey and Development Agency (GSDA) based on the guidelines given by the Groundwater Estimation Committee (GEC-1997) constituted by Ministry of Water Resources (Government of India).
Maps generated from the integration of water level data of Central Ground Water Board and State Ground Water Board
Posted on 17 Jul, 2011 03:49 PMThe CGWB under the Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India, is the national apex agency entrusted with the responsibilities of providing scientific inputs for management, exploration, monitoring, assessment, augmentation and regulation of ground water resources of the country.
Down the drain – Exploring traditional water systems - A film by Tarun Jayaram
Posted on 21 Jun, 2011 10:41 AM
down the drain from tarun jayaram on Vimeo.
These are some of the questions which led Tarun Jayaram, the film-maker to explore traditional water systems in the country. From the documentary’s opening moments, the director engages us with a beautifully shot array of footages ranging from pilgrims taking a holy dip of Ganges to beautiful baolis and tankas of Rajasthan to the ancient town of Hampi in Karnataka, while establishing how rivers have been an integral part of Indian culture and how its rich tradition of harvesting rainwater needs to be re-established to deal with the present day water crisis. Over the refreshing images and soothing audio, it advocates the need for community participation in rejuvenating the traditional methods of rainwater harvesting.
Guidelines for successful well site selection – A paper in Current Science
Posted on 16 Jun, 2011 07:57 PMGroundwater is a natural replenishable resource. It is an important source for various purposes, including drinking, irrigation and industrial, due to insufficient surface water supply and frequent failure of monsoon. Identification of groundwater zones depends upon many factors such as distribution of rainfall, runoff, grain size of soil, topographic features, type of landform, drainage conditions, lithological characteristics, land use practices, depth to groundwater level and environmental constraints, which are not uniform in any area.

Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons
Pampered views and parrot talks – In the cause of well irrigation in India – A paper by Institute for Resource Analysis and Policy
Posted on 15 May, 2011 06:14 PMIt is widely held that surface irrigation is becoming increasingly irrelevant in India’s irrigation landscape in spite of increased investments, and therefore future investments in irrigation should be diverted for well irrigation.
Jalyatra: Exploring India's traditional water management systems
Posted on 14 May, 2011 07:34 PM Jalyatra - Exploring India's traditional water management systems, by Nitya Jacob is an ecological travelogue that looks at links between water, society and places It describes in detail what existed, how it fitted into the socio-cultural milieu and was appropriate for the local climate and geography. It then examines reasons for their decline, as indeed most have, in recent decades.
Jalyatra - Exploring India's traditional water management systems, by Nitya Jacob is an ecological travelogue that looks at links between water, society and places It describes in detail what existed, how it fitted into the socio-cultural milieu and was appropriate for the local climate and geography. It then examines reasons for their decline, as indeed most have, in recent decades.
While recording the dismal state of traditional systems, the author stumbles upon small initiatives that have brought about significant transformation across regions. It refers to noisy hidrums and gharaats, the river-run flour mills of Uttaranchal, the technologies whose potential has yet to be fully realised. It looks at water harvesting structures of southern India—the eris and ooranis. However, it admits that the average person is singularly uninterested in protecting the environment.
Jalyatra captures the efforts of NGOs and enlightened individuals striving to revive these systems. It makes the case for a mass movement to revive traditional water management systems, especially village ponds, across the country as the way to ensure water security in India. In Chambal, the author meets Brij Mohan Gujjar, dacoit turned water conservationist, who is doing valuable work on the check dams designed to control the flow of water in the ravines; and in Shillong, Lan Potham shows him the uses of the easily available bamboo to construct the shyngiar which irrigates his areca nut plantation.
Between the city and the salty sea - The wells of Bhuigaon, Thane, Greater Mumbai - Guest post by MS Gopal
Posted on 22 Apr, 2011 05:57 PMAs the concrete jungle of Greater Mumbai reaches Bhuigaon and overuse of groundwater sucks in the sea water, the traditional wells are under threat.




