Treatment and Purification
Solar and wind based freshwater, saltwater and brackish water purification systems
Posted on 05 Feb, 2012 07:12 PMArticle Courtesy: Trunz Water Systems
Global change, wastewater and health in fast growing economies - Paper published in the journal Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability
Posted on 02 Feb, 2012 11:35 AMIt argues that among the water challenges in the 21st century, the water quality health nexus is one of the most serious challenges that will need to be addressed at an urgent level.The paper directs attention at the rapid and unequal growth and development patterns emerging in developing economies and the impact of this development on the environment and human populations. The paper directs attention to the negative impact of this development on one of the important natural resources such as water and the linkages between water quality and public health of populations.
Strengthening quality monitoring to provide safe drinking water: Common treatments and analyses
Posted on 30 Jan, 2012 10:59 AMAuthor : Ravi Savant
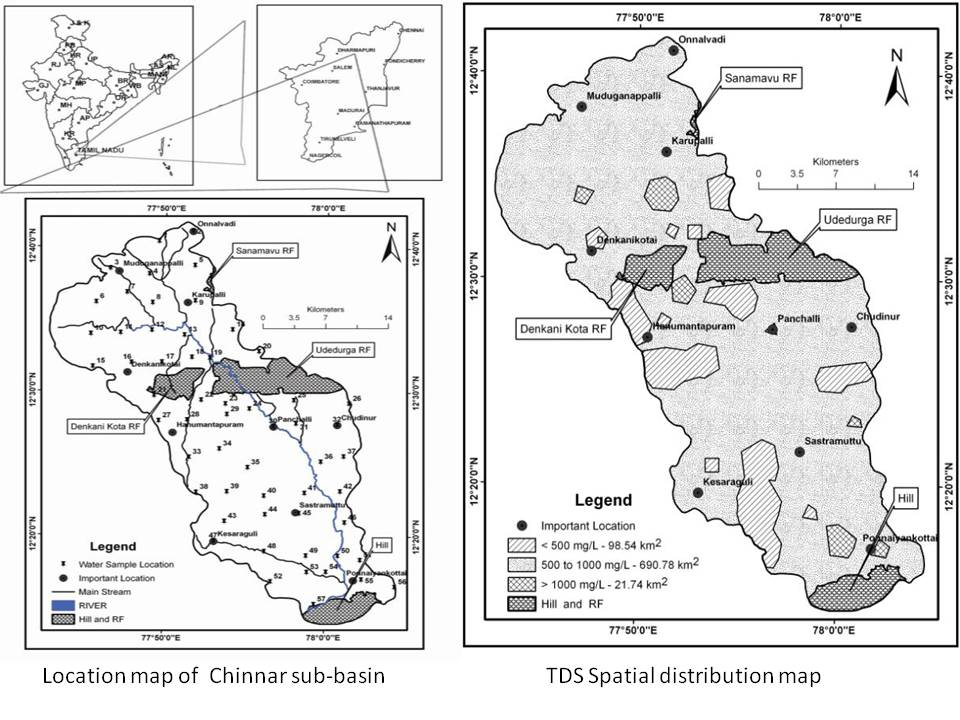
Evaluation of physico-chemical characteristics in groundwater using GIS – A case study of Chinnar sub-basin, Cauvery River, Tamil Nadu, India
Posted on 20 Jan, 2012 04:26 PMThe study found that the groundwater of the basin is extremely hard with total hardness, magnesium and potassium contents being above the permissible limits. Thirty nine out of 57 samples exceed the allowable limits for fluoride.
India Water Expo, March 1-3, 2012, Ahmedabad
Posted on 20 Jan, 2012 09:05 AMOrganizer: ASSOCHAM,
EverythingAboutWater
Venue: Gujarat University Exhibition Hall, Ahmedabad

Description:
India Water Expo - the exclusive trade show on Indian Water Industry will next take place in Ahmedabad (1-3 March, 2012).The event will showcase latest offerings in water market and help bridge knowledge gaps on water & wastewater management for users industries. As a cost effective marketing platform for key players, India Water Expo ensures that you reach your target customers in India. Manufacturers specializing in water treatment, wastewater management and all other related industries can showcase and exhibit their products and expertise.
India Water Expo, April 27-29, 2012, Chennai
Posted on 20 Jan, 2012 09:02 AMOrganizer: ASSOCHAM,
EverythingAboutWater
Venue: Chennai Trade Centre, Chennai

Description:
India Water Expo - the exclusive trade show on Indian Water Industry will next take place in Chennai (27-29 April, 2012). The event will showcase latest offerings in water market and help bridge knowledge gaps on water & wastewater management for users industries. As a cost effective marketing platform for key players, India Water Expo ensures that you reach your target customers in India. Manufacturers specializing in water treatment, wastewater management and all other related industries can showcase and exhibit their products and expertise.
Groundwater hydrology and groundwater quality in and around Bangalore city - Department of Mines and Geology (2011)
Posted on 19 Jan, 2012 11:04 AMEarlier studies carried out by the Department of Mines and Geology during 1994, 1995 and 2003 on the groundwater quality of Bangalore Metropolis had found that the groundwater pollution in the city has mainly been due to sewage disposal and recommendations have been made to prevent pollution from sewage and industrial wastes.
The unquiet river: An overview of select decisions of the courts on the river Yamuna
Posted on 14 Jan, 2012 06:40 PMThe river has attained the distinction of being perhaps the river attracting the most judicial attention in india, after the Ganga. This report analyses the various laws and judicial decisions pertaining to the Yamuna and their effects on the river.
Sustainable groundwater management – Report of the Working Group of the Planning Commission for the 12th Five Year Plan
Posted on 06 Jan, 2012 04:27 PMThe existing methodology of groundwater resources assessment is appropriate and suitable for country-wide groundwater resources estimation, considering the present status of database available with the Central and State agencies.
Living rivers, dying rivers: Bagmati river in Nepal
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 06:07 PMBagmati river in Kathmandu: From holy river to unthinkable flowing filth
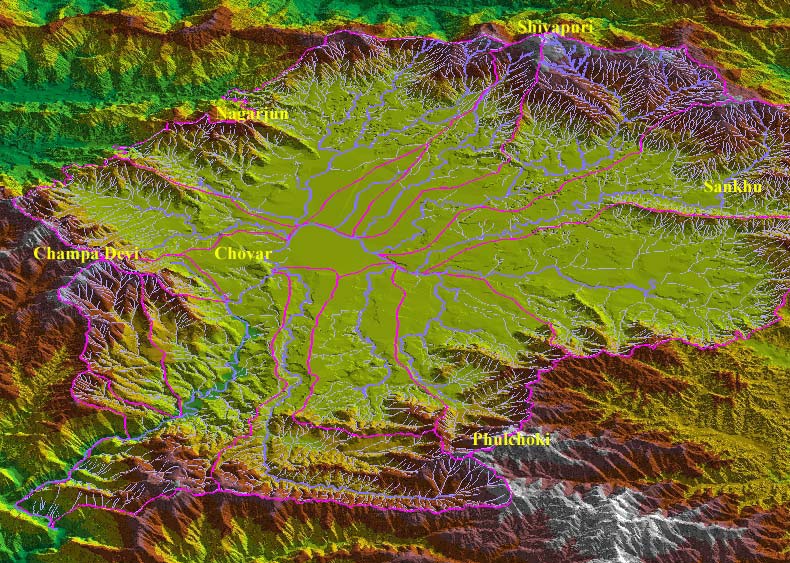
Ajaya Dixit initiated his presentation with a general account of how rivers shape the landscape and how riverine ecosystems have nurtured society and kept civilisations vibrant, cultured and creative. Dixit went on to discuss the basin characteristics of the Bagmati, a tributary of the Kosi that rises in the Shivapuri hills, north of the Kathmandu valley. Around fifteen percent of the basin area (3700 sqkm) lies in Nepal, while the remaining is in India. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1400 mm and is more than 2000 mm in the hills. Bagmati is a seasonal river with rainfall and springs as its main source. Its mean flow is 15.6 cubic metre/second and low flow is 0.15 cubic metre/second in April.
Kathmandu lies in the Upper Bagmati basin and studies suggest that an ancient lake called the Paleo-Kathmandu lay within the Kathmandu valley as a lacustrine formation. Early settlers lived in lower slopes and used springs and river in the upper reaches. When they moved to the valley floor, they built dongia dharas, which are stone water spouts fed by the unconfined aquifers and delivered water through surface channels. Even today, dongia dharas dated back to 1500 years exist. The state built canals (raj kulo) tapped the upper stretches of the rivers close to the mountains. Rivers and irrigation helped recharge aquifers and ponds.
However, rising urbanisation has damaged these ancient artifacts. Over the last sixty years Kathmandu has expanded massively and its population has increased from 0.41 million in 1951 to 2.6 million in 2011. The city has a huge transient population aside from this, reducing it to a concrete nightmare. Seismologists suggest that Kathmandu is a rubble city in the making. Though the Bagmati river flow has not changed significantly in the last seventy years, the character of the river has been transformed significantly during the period 1970 to 1990. The river has been canalised while the dumping of the city’s garbage into it continues. Dixit identified a plethora of problems faced by the river such as upstream water diversion for drinking water needs, disposal of untreated liquid waste, disposal of solid waste, river jacketing for roads and commercial activities, sand mining and physical encroachment.
The state of the river is an outcome of the current approach to waste management particularly liquid waste management. Three types of waste water namely yellow water flux, grey water and yellow black flux are being generated and flowing water is being used as a vehicle to dispose these. The idea of a water based disposal system e.g. flush toilet embedded in Victorian engineering has led to a technological lock-in with the result that the notion of a natural hydrological cycle has undergone a fundamental transformation.
All the same, the bulk of the load in the river is biological though there are some factories releasing effluents. In the last 20 years some of them have been closed or relocated and the river now stands a chance of being salvaged.






