Irrigation
Irrigation, power and energy resources development in India
Posted on 19 Sep, 2009 03:17 PMAll the above papers and more resources on this subject, are available at this link: http://groups.google.co.in/group/irrigation-power-energy/files?hl=en
Are Pumped Storage Schemes Beneficial For Harnessing The Krishna River Water Further (1995)
Techniques to slow runoff and erosion from steeply sloping land
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 12:37 PM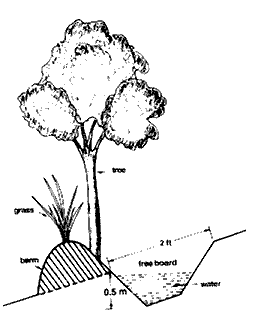 These techniques are useful to slow runoff and erosion from sloping land, and also to revegetate degraded areas. Areas with high rainfall, steep slopes, and thin soils should use slightly graded bunds / terraces / trenches to allow some drainage.
These techniques are useful to slow runoff and erosion from sloping land, and also to revegetate degraded areas. Areas with high rainfall, steep slopes, and thin soils should use slightly graded bunds / terraces / trenches to allow some drainage.
Tips for using bunds in cultivated Land
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 12:06 PMBunds have many benefits, including marking the boundaries of farm-holdings, slowing the movement of soil and water, and providing a place for integrating trees into agricultural systems. Here are some tips for using bunds within farmland:
- Cattle should be kept away from the area while establishing saplings, by using livehedge fencing. Cactus, Euphorbia spp, and Agave are useful for a livehedge fence.
- Larger trees can be planted on boundary bunds, and smaller trees which will be harvested more frequently can be planted on internal bunds, which divide one holding into separate sections.
How to restore highly degraded lands
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 11:51 AMIn places where the land is too degraded for agriculture and the soil is too shallow for bunding, rocks can be used to protect existing stumps from browsing and allow regeneration. Rock fences can also be used to protect areas planted with fodder species. Hardy, drought tolerant trees such as neem, tamarind, custard apple, acacia, and eucalyptus can be planted.
Pitcher irrigation - A method that uses round earthen containers for growing saplings
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 11:46 AM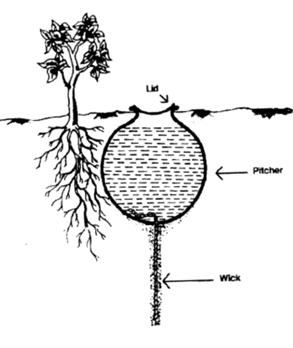 It is similar to drip irrigation, but less expensive to install. The pitchers are the round earthen containers used in rural areas for water storage, ranging from 10 to 20 liters in capacity. This kind of irrigation is ideal for spreading plants such as gourd, pumpkin, and melon because few pitchers are needed per unit area. It is also very good irrigation for saplings, promoting deep root growth.
It is similar to drip irrigation, but less expensive to install. The pitchers are the round earthen containers used in rural areas for water storage, ranging from 10 to 20 liters in capacity. This kind of irrigation is ideal for spreading plants such as gourd, pumpkin, and melon because few pitchers are needed per unit area. It is also very good irrigation for saplings, promoting deep root growth.
Agronomic measures in dryland agriculture: An overview
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 10:39 AM
Soil and water conservation measures consist of agronomical and mechanical methods. Agronomic methods are supported with mechanical measures where land slope exceeds permissible limits and runoff gains erosive velocities.
The following boxes explain the nature of agronomic measures which are essential in inter-bunded or terraced areas. These practices enhance the utility value of all kinds of mechanical structures.
How to catch rainwater where it falls - An intoduction
Posted on 14 Sep, 2009 04:39 PMPerhaps you are a farmer and you want to practice good water and soil management for your crops and trees, or you own some land and you want to manage it carefully to recharge the groundwater. You may be focusing on what you can do with your own land, or wondering what your community can do, or you may even be thinking at the watershed level.
Integrated approaches for sustainable development in water resources sector
Posted on 04 Sep, 2009 12:11 PMThe Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, Technology for Sustainable Development and the Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne EPFL have produced a report titled Integrated Approaches for Sustainable Development in Water Resources Sector.
Guidelines on various components of National Project on Organic Farming: Department of Agriculture & Cooperation
Posted on 02 Sep, 2009 11:22 AMMore crop and income per drop of water - Report by the advisory council on artificial recharge of groundwater (MoWR) (2006)
Posted on 02 Sep, 2009 11:03 AMThis report by the Advisory Council on Artificial Recharge of Ground Water, the Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India is divided into the following sections:





