Geogenic Contamination
Water quality hot-spots in rivers of India – A report by Central Water Commission
Posted on 08 Nov, 2011 01:03 PM It evolves a methodology for identifying hot spots in Indian rivers. The water quality data is based on the average values observed during the last ten years (2001-2011) at 371 monitoring stations of CWC on almost all major, medium and minor rivers in India. In respect of Dissolved Oxygen and Biochemical Oxygen Demand, the Central Pollution Control Board's classification has been considered for evaluating the hot spot in the rivers.
It evolves a methodology for identifying hot spots in Indian rivers. The water quality data is based on the average values observed during the last ten years (2001-2011) at 371 monitoring stations of CWC on almost all major, medium and minor rivers in India. In respect of Dissolved Oxygen and Biochemical Oxygen Demand, the Central Pollution Control Board's classification has been considered for evaluating the hot spot in the rivers.
The physical and chemical quality of river water is important in deciding its suitability for drinking purposes. As such the suitability of river water for potable uses with regard to its chemical quality has to be deciphered and defined on the basis of the some vital characteristics of the water. Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) vide its document IS: 10500:1991, edition 2.2 (2003‐09) has recommended the quality standards for drinking water and these have been used for finding the suitability of river water. On this basis of classification, the natural river water of India has been categorized as desirable, permissible and unfit for human consumption.
An overview of arsenic in groundwater in Tamil Nadu – A report by Water Resources Department
Posted on 26 Oct, 2011 06:03 PMNow-a-days heavy metal arsenic poses a health risk problem throughout the world. Arsenic may be found in water which has flowed through arsenic-rich rocks. Severe health effects have been observed in populations drinking arsenic-rich water over long periods in countries world-wide.
Institutionalization of users' level - Water quality monitoring and surveillance in Gujarat - A report by WASMO
Posted on 26 Sep, 2011 11:39 AMThe programme focused on community involvement in assessing and evaluating water quality.
Evaluation of Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) – A report by Indian Institute of Management Lucknow
Posted on 25 Sep, 2011 02:41 PMThis evaluation report by the Indian Institute of Management (Lucknow) of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), a central institution established to set environmental standards for all parts of the country focuses on strengthening of CPCB and its preparedness to undertake various measures as suggested by environmental statutes.
State geology and mineral maps – Geological Survey of India Miscellaneous Publication Series
Posted on 24 Sep, 2011 04:07 PMThe Geological Survey of India (GSI) has been preparing state geology and mineral maps as a part of its Miscellaneous Publications series from time to time. During the span of three and a half decades since the first edition was published, enormous knowledge has been added in the sphere of geology of the areas necessitating revisions. The entire modified and updated series published at various points of time is available here.
Groundwater quality assessment of Jharia coalfield area in West Bengal - A case study in NISCAIR
Posted on 27 Aug, 2011 06:35 PMThis case study in National Institute of Science Communication and Information Resources (NISCAIR) by the Central Institute of Mining and Fuel Research (CIMFR), Dhanbad and the Geo-Environment Division (Environment Management Group) deals with groundwater quality assessment of Jharia coalfield area of West Bengal. The physiochemical characteristics of groundwater of the upper catchments of the coalfield were studied to evaluate the water quality.
Water quality study and cost-benefit analysis of rainwater harvesting in Kuttanad, Kerala
Posted on 25 Aug, 2011 02:23 PM This thesis by Christina Tang for the Center of Environmental Studies, Brown University deals with a study of water quality and attempts to ascertain the net benefits or costs from rainwater harvesting under a variety of scenarios for households in various water supply conditions.
This thesis by Christina Tang for the Center of Environmental Studies, Brown University deals with a study of water quality and attempts to ascertain the net benefits or costs from rainwater harvesting under a variety of scenarios for households in various water supply conditions.
Eighty percent of the 7,00,000 citizens of Kuttanad, a region in the coastal State of Kerala have no access to clean water. In Kuttanad, intensive untreated human sewage and agricultural activities have caused severe surface water contaminations. At the same time, other sources of freshwater are unreliable for drinking: groundwater is acidic due to the soil conditions and iron leaching; freshwater from public tap is infrequent; and water supply from private vendors is extremely expensive.
Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission – Report of an evaluation study by the Planning Commission (2010)
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 10:17 PMThis evaluation study report by the Programme Evaluation Organisation, Planning Commission attempts to document the major achievements in rural water services under Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission. It does so by assessing the extent of coverage and access to improved services in the rural areas.
Challenges of sustainable water quality management in rural India - Current Science
Posted on 23 Aug, 2011 04:51 PM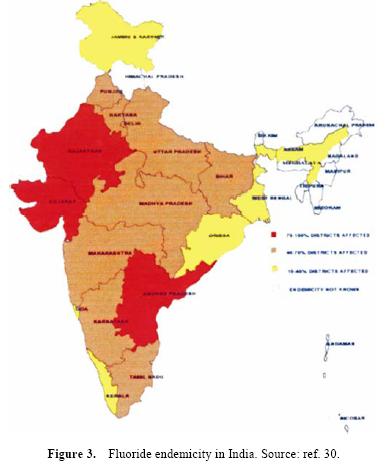 The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
The article informs that access to safe drinking water remains an urgent necessity, as 30% of urban and 90% of rural households still depend completely on untreated surface or groundwater.
While access to drinking water in India has increased over the past decade, the tremendous adverse impact of unsafe water on health continues. It is estimated that about 21% of communicable diseases in India are water related.
Although some degree of intervention in terms of chlorination and monitoring of water quality exists in major cities and towns, rural India, which constitutes the bulk (70%) of the population, is usually deprived of such interventions. The population in rural India is mainly dependent on the groundwater as a source of drinking water. As a quality concern the groundwater is often found to be contaminated with fluoride, arsenic, iron and salts. In recent years, fluorosis has emerged as major public health issue in rural India.
Water quality status of rivers in India – Report of Central Water Commission
Posted on 15 Jul, 2011 06:19 PMThe Level-I Laboratories are located at 258 field water quality monitoring stations on various rivers of India where physical parameters such as temperature, colour, odour, specific conductivity, total dissolved solids, pH and dissolved oxygen of river water are observed.





