Droughts and Floods
New water policy more contentious; least helpful in tackling existing issues
Posted on 22 Feb, 2012 12:34 PMAuthor : Dr. Arvind Kumar
Rural water access: Governance and contestation in a semi-arid watershed in Udaipur, Rajasthan: A paper in EPW
Posted on 21 Feb, 2012 05:19 PMStudy area
This study is carried out in micro-watershed No.19, which comprises six villages in Jhadol tehsil of Udaipur district in Rajasthan. A minor irrigation project completed in 1980 serves these six villages
Rainfall, storage levels in reservoir and groundwater use
Towards greener development: EIA sector specific manuals brought out by the Ministry of Environment and Forests
Posted on 19 Feb, 2012 07:20 PMThese manuals are aimed at expert appraisal committees, and hope to improve the quality of appraisal of projects. These will also provide a template for use by organisations and consultants developing the EIA reports.
Social exclusion in watershed development: Evidence from the Indo-German watershed development project in Maharashtra - A LEAD paper
Posted on 18 Feb, 2012 03:08 PMMarginalized communities are excluded from a say in the creation of policies.
Climate change risk - An adaptation and mitigation agenda for Indian cities - A paper published in the journal Environment and Urbanisation
Posted on 18 Feb, 2012 01:33 PMThe paper dwells on the likely changes that climate change is expected to bring in temperature, precipitation and extreme rainfall, drought, river and inland flooding, storms/storm surges/coastal flooding, sea-level rise and environmental health risks, and who within urban populations will be at risk.
Multi-stakeholder dialogue is messy, but necessary
Posted on 16 Feb, 2012 01:32 PMA workshop on ‘Understanding and resolving water conflicts in the North East India', was organized by Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts in India (Forum), in collaboration with Aaranyak (Guwahati), Centre for the Environment, IIT (Guwahati), Arghyam (Bangalore), SaciWATERs-CapNet Network (SCaN) and Cap-Net to discuss emerging issues related to water conflicts and their resolution in the region. This workshop was held in Guwahati on January 23-26, 2012. It aimed at presenting concepts and theory related water conflicts as well as issues especially relevant to the North East Region.
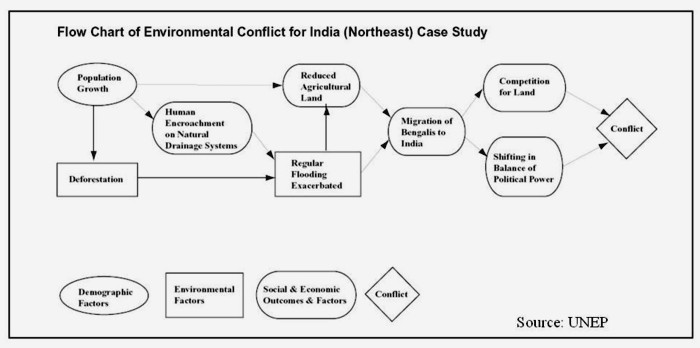
"Understanding and resolving water conflicts in the North East": Workshop held at Guwahati, 23-26 January 2012
Posted on 16 Feb, 2012 01:31 PMGuest post by: Raju Mimi
Climate change adaptation in Himachal Pradesh - Sustainable strategies for water resources - A report by the ADB
Posted on 16 Feb, 2012 10:29 AMIt includes the present and planned water utilisation across sectors and uses, within a framework of environment, conservation and sustainability. It also examined the present institutional arrangements for water resources management and assessed the requirements for institutional development, improvement in data collection and analysis, catchment and agriculture planning, and other reforms required to ensure sustainable water resources management.
Climate: Observations, projections and impacts - India - A report by the Met Office (UK)
Posted on 15 Feb, 2012 03:25 PMThis was done as a part of a project that aimed at compiling scientifically robust and impartial information on the physical impacts of climate change for more than 20 countries.
Living rivers, dying rivers: Rivers in the Western Ghats
Posted on 10 Feb, 2012 04:12 PMRiver stories from Maharashtra: Many morals to learn
Parineeta Dandekar’s presentation began with an account of some statistics related to Maharashtra, the third largest state in India. Regarding the state of water resources in Maharashtra, she noted that of the five river basin systems, 55 percent of the dependable yield is available in the four river basins (Krishna, Godavari, Tapi and Narmada) east of the Western Ghats. These four river basins comprise 92 percent of the cultivable land and more than 60 percent of the population in rural areas. 45 percent of the state's water resources are from west flowing rivers which are mainly monsoon specific rivers emanating from the Western Ghats and draining into the Arabian Sea.
With 1821 large dams and more in the offing, Maharashtra has the maximum dams in the country (35.7%). However, the proportion of gross irrigated area vis a vis the gross cropped area at 17.8 percent is much lower than the national average of 44.6 percent. The contradictions from the state, which is home to the highest number of dams, were discussed. In nearly 70 percent of the state’s villages (around 27,600 villages), water is either not available within 500 metres distance, or within 15 metres below ground level or when available is not potable (World Bank, Promoting Agricultural Growth in Maharashtra, Volume 1, 2003).
Dandekar discussed the World Bank funded Maharashtra Water Sector Improvement Project (MWSIP) initiated in 2005 whose main components were establishment, operationalisation and capacity building of Maharashtra Water Resources Regulatory Authority (MWRRA); establishment of river basin agencies in Maharashtra; and restructuring and capacity building of the Water Resources Department. The MWRRA Act (2005) has been amended, taking out the clause for equitable water distribution, and granting the Cabinet the rights to have the last say about water entitlements. This has led to a diversion of water for irrigation from the vulnerable, suicide-prone Vidarbha region to thermal power plants. According to Prayas, “entitlements of more than 1500 MCM have been changed from agriculture to industries and cities”.





