Research Papers
Interdisciplinary approach to water management: From the uplands to the coast - The Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna Basin
Posted on 30 Dec, 2011 11:04 AMIn this paper, Jayanta Bandopadhyay explains the need for an interdiscipliinary framework for water resource management. He states that this framework needs to include ecological, social, economic and institutional perspectives. These perspectives are essential to facilitate cooperation over the management of transboundary rivers.
Managing natural resources through simple and appropriate technological interventions for sustainable mountain development - Current Science (2011)
Posted on 30 Dec, 2011 10:07 AMThe initiative on management of natural resources through appropriate interventions aimed at:
Life, livelihoods, ecosystems, culture: Entitlements and allocation of water for competing uses
Posted on 27 Dec, 2011 05:10 PM This report has been prepared by the members of the working group set up by the Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts in India on the issue of “Entitlements and allocations for livelihoods and ecosystem needs". The introductory chapter sets out the context of the report. The immediate context is the work of the Forum over the last 4-5 years, and the learning that this particular issue leads to many water conflicts in India.
This report has been prepared by the members of the working group set up by the Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts in India on the issue of “Entitlements and allocations for livelihoods and ecosystem needs". The introductory chapter sets out the context of the report. The immediate context is the work of the Forum over the last 4-5 years, and the learning that this particular issue leads to many water conflicts in India.
Agriculture, food security and nutrition in Vidarbha: Household level analysis – A special article in EPW
Posted on 27 Dec, 2011 09:43 AMUsing the data generated from a baseline survey on a sample of 6,990 households covering six districts, this paper attempts to assess the relationships between agriculture, food security and nutrition for children, adolescents and married women of reproductive age.
The impacts of water infrastructure and climate change on the hydrology of the Upper Ganges river basin – A research report by IWMI
Posted on 18 Dec, 2011 07:03 PM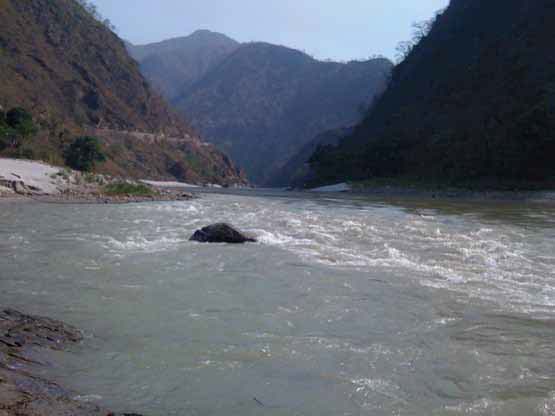 The Ganges river system originates in the Central Himalayas, and extends into the alluvial Gangetic Plains and drains into the Indian Ocean at the Bay of Bengal. In the upstream mountainous regions, hydropower is the main focus of development with mega and micro projects either under construction or being planned in both Nepal and India.
The Ganges river system originates in the Central Himalayas, and extends into the alluvial Gangetic Plains and drains into the Indian Ocean at the Bay of Bengal. In the upstream mountainous regions, hydropower is the main focus of development with mega and micro projects either under construction or being planned in both Nepal and India.
After the main river channel reaches the plains, it is highly regulated with dams, barrages and associated irrigation canals. All this infrastructure development and abstractions affects the river’s flow regime and reduces flows, which, in turn, impacts downstream water availability, water quality and riverine ecosystems. Furthermore, there are concerns that climate change is likely to exacerbate the water scarcity problem in the Ganges Basin. Therefore, modeling the hydrology of the basin is critical for estimation, planning and management of current and future water resources.
Strengthening rural livelihoods – A report by IDRC
Posted on 13 Dec, 2011 05:17 PM This report prepared by International Development Research Centre (IDRC) examines how information related constraints in poor rural areas are being overcome and how information technology is being employed to the benefit of people in South Asia.
This report prepared by International Development Research Centre (IDRC) examines how information related constraints in poor rural areas are being overcome and how information technology is being employed to the benefit of people in South Asia.
Poor people are constrained by limited access to information and poor communications technology. The research looked at the use of ‘information communications technologies’ (ICTs) in providing agricultural extension services, getting timely market price information, finding out about rural wage labour opportunities, helping rural communities to build a sustainable asset base and understanding crop diseases and soil nutrition.
The results of the research bring together rigorously tested practices and methods of applying ICTs for improving rural livelihoods. Each research study has investigated how and to what extent a specific ICT intervention made a difference. Together it shows how ICTs have empowered rural people and transformed livelihoods in agriculture: by filling information gaps, raising awareness, building skills and extending social networks.
The focus was on agricultural communities, as Asia’s poor and middle-income countries have primarily agriculture-based economies. However, a broader ‘livelihoods’ approach has been taken to ensure that we observe the variety of ways ICTs can have an effect on rural communities. The scope of the research took into account the range of on-farm and off-farm productive and reproductive activities that support farming households and communities.
Performance audit of food security schemes in Orissa and Uttar Pradesh – A report by Centre for Environment and Food Security
Posted on 13 Dec, 2011 04:55 PMThe schemes covered under this audit include, (a) Public Distribution System (PDS), (b) Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY), (c) Mid-day Meals (MDM), (d) Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), (e) National Old Age Pension Scheme (NOAPS), (f) National Family Benefit Scheme (NFBS), (g) Annapurna, (h) National Maternity Benefit Scheme (NMBS), (i) Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY), and (j) National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS).
Comparative management performance of government and farmer managed irrigation systems in Kashmir
Posted on 04 Dec, 2011 11:49 AMKashmir was originally home to an elaborate network of farmer owned and managed canal based irrigation systems. Gradually, with the increase in planned development, several irrigation canals were taken under the control of the irrigation department. This paper compares the management of irrigation systems by farmers and government.

Status of groundwater quality in India - Report of the survey conducted in metropolitan areas by the CPCB
Posted on 24 Nov, 2011 05:36 PMThe report recognises that most groundwater quality problems are anthropogenic in origin, caused by a combination of over-exploitation and infiltration of wastes. Inadequate infrastructure and resources mean that waste generated by cities and industrial areas is not properly collected, treated and disposed, thus leading to grondwater contamination.
Status of water treatment plants in India - A report on their operational status by the Central Pollution Control Board
Posted on 23 Nov, 2011 11:47 AMThis document by the Central Pollution and Control Board (CPCB) describes the findings of a study that evaluated water treatment plants located across the country, for prevailing raw water quality, water treatment technologies, operational practices, chemical consumptio