rajshekar
How to control gully erosion
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 12:58 PM Over the years, unchecked soil erosion can lead to the formation of deeper and deeper gullies. There are several methods for controlling gully erosion, which can be chosen depending on the materials available.
Over the years, unchecked soil erosion can lead to the formation of deeper and deeper gullies. There are several methods for controlling gully erosion, which can be chosen depending on the materials available.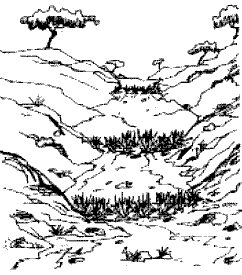
If it is a small gully, vegetation can be planted in strips across the gully to slow the velocity of water, trap silt, and prevent further erosion.
Techniques to slow runoff and erosion from steeply sloping land
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 12:37 PM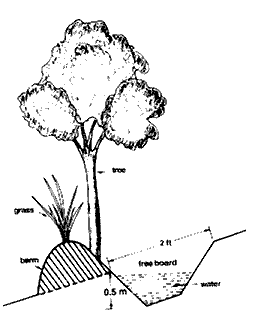 These techniques are useful to slow runoff and erosion from sloping land, and also to revegetate degraded areas. Areas with high rainfall, steep slopes, and thin soils should use slightly graded bunds / terraces / trenches to allow some drainage.
These techniques are useful to slow runoff and erosion from sloping land, and also to revegetate degraded areas. Areas with high rainfall, steep slopes, and thin soils should use slightly graded bunds / terraces / trenches to allow some drainage.
Tips for using bunds in cultivated Land
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 12:06 PMBunds have many benefits, including marking the boundaries of farm-holdings, slowing the movement of soil and water, and providing a place for integrating trees into agricultural systems. Here are some tips for using bunds within farmland:
- Cattle should be kept away from the area while establishing saplings, by using livehedge fencing. Cactus, Euphorbia spp, and Agave are useful for a livehedge fence.
- Larger trees can be planted on boundary bunds, and smaller trees which will be harvested more frequently can be planted on internal bunds, which divide one holding into separate sections.
How to restore highly degraded lands
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 11:51 AMIn places where the land is too degraded for agriculture and the soil is too shallow for bunding, rocks can be used to protect existing stumps from browsing and allow regeneration. Rock fences can also be used to protect areas planted with fodder species. Hardy, drought tolerant trees such as neem, tamarind, custard apple, acacia, and eucalyptus can be planted.
Pitcher irrigation - A method that uses round earthen containers for growing saplings
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 11:46 AM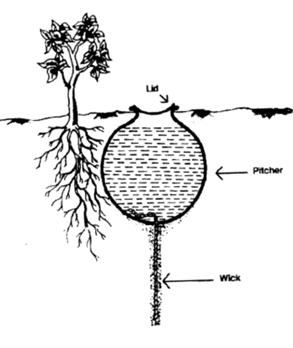 It is similar to drip irrigation, but less expensive to install. The pitchers are the round earthen containers used in rural areas for water storage, ranging from 10 to 20 liters in capacity. This kind of irrigation is ideal for spreading plants such as gourd, pumpkin, and melon because few pitchers are needed per unit area. It is also very good irrigation for saplings, promoting deep root growth.
It is similar to drip irrigation, but less expensive to install. The pitchers are the round earthen containers used in rural areas for water storage, ranging from 10 to 20 liters in capacity. This kind of irrigation is ideal for spreading plants such as gourd, pumpkin, and melon because few pitchers are needed per unit area. It is also very good irrigation for saplings, promoting deep root growth.
Extensive online resource base on the System of Rice Intensification: Homepage on the CIIFAD website
Posted on 29 Aug, 2009 10:31 AMThe site has sections detailing the methodology of SRI, its advantages, origins, current status in countries across the world, videos, articles, research papers, extension information, conference outputs, discussion communities, update series, newsletters and more.
See the homepage: Here
Rainwater harvesting made mandatory in Andhra Pradesh: All Municipal Corporations and Urban Development authorities directed to implement provisions
Posted on 21 Aug, 2009 02:38 PMThis government order on the rainwater harvesting website of Centre for Science and Environment makes rainwater harvesting mandatory in all Municipal Corporations, Urban Development Authorities and Municipalities, buildings with an a
Augmenting groundwater: The basics on how to construct a recharge well
Posted on 20 Aug, 2009 05:10 PM

Informative and detailed slideshows on all things related to household rainwater harvesting
Posted on 20 Aug, 2009 04:34 PMSeven easy steps to constructing a recharge pit
Read More
The making of a recharge well
Read More
Rainwater harvesting basics: Filtering the water before storage and use
Posted on 19 Aug, 2009 03:29 PMOverview
Rainwater is amongst the purest water one can get distilled as it is by the sun. However, in a rainwater harvesting system, the water comes in contact with several surfaces, such as the roof or gutters. Its flow becomes possibly mixed with leaves or dust.