Advanced Centre for Water Resources Development and Management (ACWADAM)
Hydraulic conductivity: The ability of the rock material to allow the flow of groundwater – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 27 Aug, 2010 08:10 AM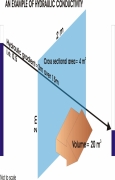 This presentation by ACWADAM on hydraulic conductivity deals with the hydrologic properties of rocks that signify the status of a rock as a good or poor aquifer. The status of a rock with regard to groundwater occurrence and movement is decided by its porosity (specific yield, more practically) and its hydraulic conductivity. These properties decide whether a rock can store and transmit groundwater.
This presentation by ACWADAM on hydraulic conductivity deals with the hydrologic properties of rocks that signify the status of a rock as a good or poor aquifer. The status of a rock with regard to groundwater occurrence and movement is decided by its porosity (specific yield, more practically) and its hydraulic conductivity. These properties decide whether a rock can store and transmit groundwater.
Hydraulic conductivity is also commonly called as permeability of the rock or rock material and is its ability to allow the flow of groundwater through it. A rock with good hydraulic conductivity allows groundwater to easily flow through it.
The presentation describes Darcy’s Apparatus, which comprises of a glass cylinder filled with porous sand. The glass cylinder with the sand bed had an inlet for inflow of water and an outlet for outflow of water. Two vertical glass tubes (manometers) are fitted in the sand tube placed at a fixed distance from each other to measure the respective levels (hydraulic heads).
Karst Hydrogeology – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 27 Aug, 2010 12:42 AMThis presentation by ACWADAM deals with Karst hydrogeology, a term used to denote the topography over limestones, dolomites or gypsum rich rocks where there are sinkholes, caverns and lack of surface streams. Karst mainly refers to carbonate rocks: Limestones (CaCO3) or Dolomites (MgCa[CO]).
The formation of carbonate rocks can be traced to physical and chemical deposition. Physical deposition is clastic in nature formed by deposition of particles carried in suspension. It is marked by higher primary porosity and low secondary porosity. Chemical deposition is in the form of precipitate formed by deposition of particles from solution. Contrary to physical deposition it is marked by low primary porosity and high secondary porosity.

Points of groundwater discharge: Types of springs – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 26 Aug, 2010 08:52 PMThis presentation by ACWADAM deals with springs, their characteristics and types. Springs are indicated by locations or points on the ground surface, where water from beneath the ground emerges on to the surface. A common example is of an overflowing unconfined aquifer.
Some of the characteristics of springs are:
- Discharge from spring may be constant or variable.
- Springs can be perennial or seasonal.
- Discharge from a spring may vary between from a trickle to about 100 cum per second.
- Difficulty in access.
- Variation in discharge.
- Temperature of spring water may vary from mean atmospheric temperature to lower or higher, even boiling temperatures. Hot quality water springs are common to many parts of the world.

Pani Panchayat: A model of groundwater management – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 25 Aug, 2010 08:20 AM The presentation by ACWADAM deals with Pani Panchayats as a model of groundwater management.
The presentation by ACWADAM deals with Pani Panchayats as a model of groundwater management.
Pani Panchayat is the name first given to a movement by Mr. Vilasrao Salunke for motivating farmers of Naigaon village of the drought-prone Purandhar taluka of Maharashtra in 1974. The government's inability to deal with the drought situation prompted him to take a 40 acre land on lease from the village temple trust and develop a recharge pond in the recharge area of the village, a dug well in the discharge zone and a lift irrigation system.
Farmers got impressed with the results demanding a scale up of the experiment leading to the setting up of Gram Gaurav Pratisthan (GGP) through which the work was expanded to encompass both groundwater and surface water management.
Measurement of weather parameters: Data collection and analysis – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 24 Aug, 2010 09:29 PMThe presentation by ACWADAM deals with measurement of weather parameters and outlines the methods used in weather related data collection and analysis. Weather information is necessary for the planning and implementation of watershed programmes, especially in understanding factors like groundwater recharge, the relationship between recharge & discharge and in aspects like irrigation planning.
Augmenting groundwater resources by artificial recharge: A case study of Kolwan valley by ACWADAM
Posted on 24 Aug, 2010 04:19 PMThe presentation by ACWADAM deals with a case study of augmenting groundwater resources by artificial recharge in Kolwan valley, Mulshi taluka, Pune. The DfID funded project was undertaken by the British Geological Survey in collaboration with its partners in India from 2002–2005. The objectives of the study were:
- Improved knowledge of the impacts of managed aquifer recharge in different physical and socio-economic settings.
- Guidance on scope and effectiveness of managed aquifer recharge for implementers, funders and policy makers.
- Dissemination of knowledge.
Pumping tests on wells: A means of measuring the storage and transmission properties of aquifers
Posted on 24 Aug, 2010 10:03 AMThe presentation by ACWADAM is part of the training module developed by them on “Planning, development and management of groundwater with special reference to watershed management programmes”. Pumping a well and observing the effect of such pumping on the water level in the pumped well as well as in the adjoining parts of the aquifer through observation wells is the basic procedure involved in a pumping test.
Hydrogeological studies for improved groundwater management strategies in the dryland areas underlain by Deccan basalts - ACWADAM
Posted on 02 Mar, 2010 05:18 PMRapid geohydrological appraisal of Purainee and Orlaha villages,Bihar - Drinking water management and alternative sources
Posted on 19 Nov, 2009 02:40 PMThis report by ACWADAM based on a rapid hydro-geological appraisal of 2 villages, in Supaul distict in flood-prone North Bihar, gives a good understanding of local conditions as well generates a lot of useful data, that can help in planning groundwater management interventions in a village. Such information is crucial especially for regions such as North Bihar, where current data about the local conditions are literally absent.
A multimedia course on groundwater management by Advanced Centre for Water Resources Development and Management (ACWADAM), Pune
Posted on 15 May, 2009 01:07 PMThis multimedia course developed by ACWADAM, Pune, is primarily meant for people working in watershed and agriculture projects, to give them a better understanding of groundwater.