The most effective means of consistently ensuring the safety of drinking water supply is through the use of a comprehensive risk assessment and management approach, that encompasses all steps in water supply from catchment to consumer. Such approaches are called Water Safety Plans (WSPs).
The aim of a WSP is to organize and systematize records of management practices applied to drinking water and to ensure workability of such practices to organized drinking water supply.
Major objectives of a water safety plan are:
- Prevent contamination of sources,
- Treat the water to remove contamination to the extent necessary to meet the water quality targets, and
- Prevent re-contamination during storage, distribution and handling.
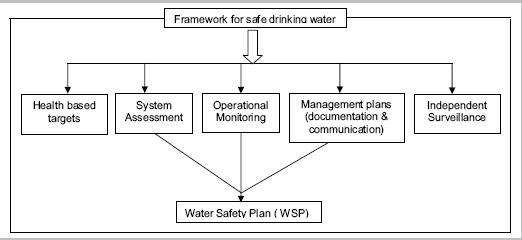
The aim of this manual is to facilitate development of WSPs focusing particularly on organized water supplies managed by a water utility. The three key components of WSPs are guided by health-based targets and overseen through drinking water supply surveillance. These are:
- System assessment,
- Identification of control measures, and
- Management plans.
The manual has attempted to delineate different aspects of WSP using the diverse setup and variable situation in Hyderabad city.
 Three pilot areas chosen for this study in Hyderabad are Adikmet Sub zone–I, Moinbagh (under Balapur service reservoir) and Serilingampally (Chandanagar area).
Three pilot areas chosen for this study in Hyderabad are Adikmet Sub zone–I, Moinbagh (under Balapur service reservoir) and Serilingampally (Chandanagar area).
There is 24X7 water supply to Adikmet area, Moinbagh is thickly populated area with old pipelines, narrow lanes and intermittent water supply whereas Serilingampally area is provided with bulk supply by HMWSSB and distributed by the Municipal Corporation.
Download Water Safety Plan: A manual for pilot study areas of Hyderabad, from the WHO India website.