All these decades from early twentieth century, storm water and artificial recharge of aquifers have seldom been an area of consideration for planners and policy makers. The country appeared to be oblivious to the fact that these too are integral part of the resources that we need to take care of before it starts hitting back at us in our daily lives! But then, such has been the case with every other resource base in India, which starts with "abundance" , runs into "shortage" and then graduates to being "scarce" and finally the "crisis" sets in.
I have to admit here that I have never been to a conference where storm water management and artificial recharge methods were discussed and deliberated upon. I have never known any urban planner or town planning agency which has put forth these considerations while developing water resource management strategies.
 Dr. S.K Jain in his talk on Storm water management, artificial recharge and improvement in ground water regime admits that a crisis is looming, with our water resources being subjected to increasing pressure. His presentation provides for an answer to the perplexing situation of alternative draught and floods, which most of our cities go through.
Dr. S.K Jain in his talk on Storm water management, artificial recharge and improvement in ground water regime admits that a crisis is looming, with our water resources being subjected to increasing pressure. His presentation provides for an answer to the perplexing situation of alternative draught and floods, which most of our cities go through.
He proposes that in designing rainwater-harvesting system, rainfall run off from the roads should be captured and through an artificial connectivity, it should be channelised to sub surface water. This approach will be effective because:
- reasonable cost
- coverage of large areas and immediate implementation
- immense benefits in terms of additional water availability
- improvement in water quality
- increased plantation, maintaining ecobalance
- lower cost of maintenance and repairs of roads
- many fold increase in life of the roads
Case Study: Road/paved area storm water recharge in industrial premises of Hero Honda Motors Limited, Dharuhera, Haryana
The plans are included in his presentation, which can be downloaded from here (pdf, 6.7mb)
Policy and regulatory guidelines have remained unelaborated in water harvesting and management. Dr.S.K Sharma's presentation on strategy and policy for artificial recharge serves as an extension to the practice of designing artificial recharge systems.
Dr.S.K Sharma in conversation
Traditional water harvesting in India dates back to IndusValley Civilizationand Mughal Period. Rooftop Rain Water Harvesting has been adopted by several government buildings, with Shram Shakti Bhawan in New Delhi being one of the earliest. Here is a slide from Dr. Sharma's presentation.
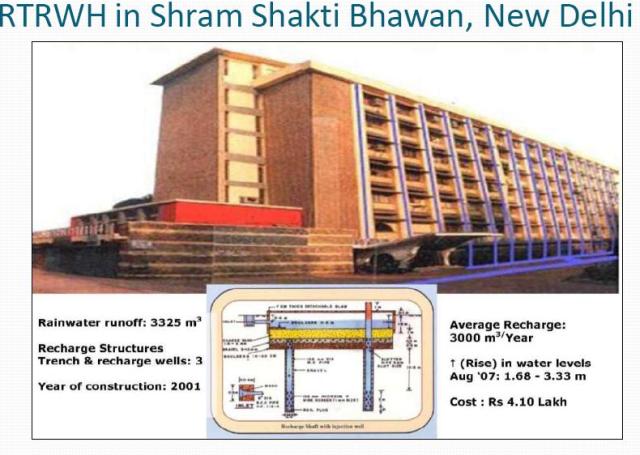
Credit: Dr.S.K Sharma
The status of legal provisions made in Rain Water Harvesting and Ground Water Recharge is:
- 18 Statesand 4UTs have made Roof TopRWHmandatory
- 4 States namely Orissa, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Jharkhand and
- 2 UTs of Lakshadweep & Andman & Nicobar Islands are in process of making such provision
- 6 States viz Chhattisgarh, Sikkim, Mizoram, Assam, Jammu & Kashmir and Manipur have yet to initiate action.
- An artificial recharge Advisory Council has be constituted in MOWR with its Minister in chair.
- The revised Ground Water Model Bill circulated by Union Govt. to Stateshave a separate chapter as guideline on RWH & Recharging.
- Need for drafting a paper on legal requirements for implementing recharge for the use of planners, environmentalist andengineers.
- Training of regulatory staff in states in assessing planning and reviewing theeffectiveness of artificial recharge scheme.
His presentation can be downloaded from here (pdf,1.3mb)