How does Land Shaping bring a change?
After implementation of LSP, a small or marginal farmer has created a plot of raised land, where rainwater cannot stagnate. At the same time he has got a pond in the same plot of land, where rainwater is stored in the monsoon season, which serves the purpose of irrigating the crops during dry months.
In view of the sustainability of the technology, the LSP model has the following practical solutions.
- Excavation of a water reservoir to store the surface water to subsequently cater to the irrigation need during second crop cultivation. The ratio between irrigated area and the pond is 4.6 : 1 (flexible) with a depth of 2.5 mt. (average).
- Introduction of double cropping; in some cases, a triple crop is also possible.
- In addition to the cropping sequence, the water reservoir is utilized for fish culture.
- Additional crop cultivation in the pond bund.
It has been demonstrated that before LSP the farmers could get only one crop throughout the year from their low-lying land. But after implementation of LSP, a plot of 0.26 ha. land (0.2 ha. raised land + 0.05 ha. pond + 0.01 ha pond bund) can generate an annual income of Rs. 5,981/-. This is an increase of 7 to 8 times of their earlier income. The income may be further enhanced depending on the cropping sequence.
Changes in cropping sequence in Land Shaping
| Prior to Land shaping | After Land Shaping |
Season – Kharif (Monsoon) Deshi Aman | Season – Kharif (Monsoon) HYV Paddy Pond Bund Vegetables (Okra, Brinjal) Banana |
Season – Rabi-Summer(Nov – May) Fallow due to non-availability of irrigation | Season – Rabi-Summer (Nov – May) Chilli, Okra, Tomato, Frenchbean, Brinjal Pumpkin, Bottlegourd, Ridgegourd, Fish culture with carp and freshwater prawn. |
How does the stored rainwater add value to mono-cropped low-lying land
This novel technology of land shaping and water storage offers farmers triple benefits in one fold:
- Double or triple cropping in the raised land
- Fish along with prawn culture in the excavated pond
- Fruit or vegetables cultivation in the pond and land embankment
Uses of water in L.S. Pond (0.05ha.)
- Total water holding capacity in pond: 11.55 acre inch.
- Fish culture and evaporation: 4.62 acre inch.(40%)
- Cultivation purpose: 6.93 acre inch (60%)
The success of the project is presented by collecting data of five years average from 100 farmers in 10 villages in an unit area of 0.26 ha. in Table 1.
Table 1:
Annual income from 0.2 ha raised land, 0.05 ha pond and 0.01 ha pond embankment and resulted increase of income after land shaping programme in comparison with the annual net income from 0.26 ha low-land before land shaping programme (figures in Rs).
| Name of the Village/Island | Av.net income from 0.2 ha.raised land in kharif season | Av.net income from 0.2 ha. Raised land in rabi season | Av.net income from 0.05 ha. Pond area | Av.net income from 0.1 ha.pond embankment | Total annual income on the averages after land shaping programme | Annual net income before land shaping programme | Resultant increase in income after land shaping programme |
| Bhangari | 2987 | 3012 | 1800 | 250 | 8040 | 690 | 12 times |
| Kaikhali 8 | 3502 | 4205 | 1790 | 210 | 9707 | 720 | 13 times |
| Kaikhali 4 | 3609 | 4303 | 1500 | 260 | 9672 | 860 | 11 times |
| Goalgange | 3808 | 4506 | 1410 | 400 | 10124 | 780 | 13 times |
| Garankhati | 3220 | 3910 | 1705 | 310 | 9145 | 903 | 10 times |
| Nolgora | 4506 | 10600 | 1508 | 410 | 17024 | 980 | 17 times |
| Chuprijihara | 4500 | 12300 | 1605 | 315 | 18720 | 920 | 20 times |
| Kantamari | 3907 | 10320 | 1809 | 210 | 10246 | 870 | 19 times |
| Ghotiharani | 3620 | 11605 | 1410 | 250 | 16885 | 900 | 19 times |
| Subhashnagar | 3675 | 8405 | 1206 | 405 | 13691 | 870 | 16 times |
LSP implemented during 1991-1992 (Impact Analysis Study . after Land Shaping)
Employment generation: Land shaping programme has proved to be a good source of income to the landless laborers of Sundarban region. It is now possible to create employment opportunities for the landless laborers in dry months (i.e. from January to June) of the year when the landless laborers cannot find any work during this period. Employment made through this programme is represented in the table 2:
Table 2: Calculation of 150 units of LSP implemented during 1994-1995
| No. of Land Shaping Programme Done | No. of days required to complete one unit | No. of Labors engaged for one employment unit | Total man-days created |
| 75(0.26 ha.) 75 (0.2 ha.) | 26 days 20 days | 360 (Average) 270 (Average) | 50,382 |
Self employment generated: Before land shaping programme, the farmers were not able to engage their labour round the year because there were no possibilities for round the year cultivation. Now, they are able to engage them into agricultural work, as there is excellent scope.
Migration: Due to enhancement of income from LSP migration has reduced to a great extent. In a survey it is revealed that 45 per cent of the beneficiaries have totally stopped to migrate to other places and 55 per cent occasionally migrate to earn additional income.
Multiple Cropping: After implementation of LSP, the former mono-cropped low-lying land, the farmers now grow two or three crops, in addition to fish in the pond and banana on the pond bund in the same piece of land in a calendar year.
Diversified Agriculture: Having raised land and assured irrigation facility, the farmers grow different vegetables, spices and oil seed in different section on the same piece of land keeping in view the demand of the market. Moreover, farmers have also been practicing duck.cum.fish culture in their ponds to minimize the cost of supplementary feed of fish.
Environmentally sound: Wide embankment surrounding the raised land protects the loss of soil erosion and plant nutrients of the cultivated land which might happen due to excessive rainfall. The land shaping plot where the farmers usually apply huge quantity of organic manure remains isolated from the chemical agriculture practiced land.
Increased family income: The income from 0.2 ha. land area has increased to the tune of 18 times in comparison to before LSP.
In addition to the above the following benefits have been documented:
- Children's care Nutritional status has improved
- Availability of fuel is little easier than before
- Women provide more assistance to their male partner in agriculture
Scaling up
SRAN has demonstrated the land shaping and water storage technique in 960 units under the Integrated Rural Development project supported by German Agro Action since 1988. Apart from this, SRAN has also implemented another 650 units of LSP.
On calculation it has been found that almost 360 man-days have been created in each land shaping area for excavating a pond. Another 120-150 additional man-days have been created for cultivation of a second crop in each LSP.
For over two decades, SRAN has been engaged in disseminating the land shaping technology and conducting participatory research. They have acquired capability and confidence to impart training to other NGOs and Government departments.
As a member of the District Planning Committee and the Sundarbans Development Board, SRAN is influencing other members to adopt the technology for large scale dissemination in the region of West Bengal to support the livelihood of distressed farming community.
Besides, SRAN has also participated in the agriculture developmental planning of West Bengal where this technology has been documented as one of the best ones for the coastal agro-climatic zone. At the annual National workshop of Krishi Vigyan Kendra held in different parts of the country, the benefits of this novel technology have been highlighted and has motivated other participants and representatives of the central Government to disseminate the same among the farming communities. In addition, SRAN also demonstrated this technology at different exhibitions at the national level.
Apart from this, SRAN also participated to the World Exhibition held at Hanover, Germany in the year 2000 to interact with experts from different countries in order to disseminate this information among the farming communities living in the same agroclimatic situation. This technology was recognized by the authority of the Exhibition as one of the best ones for livelihood of farming communities in coastal agro-climatic situations and for utilizing natural resources in an efficient way.
A Farmer's Example
The following tables present a comparative study of cropping patterns, agricultural productivity and the resultant income of a beneficiary-farmer, before and after land shaping programme.
Shri Arun Haldar, a poor farmer lived in Kaikhali Island of Sundarbans with his wife, four sons and two daughters. He had 0.26 ha low-lying cultivable land where water used to be stagnant two and a half feet during the rainy season. Haldar grew the local variety of Aman paddy during the monsoon period and was able to harvest four quintals and 80 kilogram of paddy; this was not enough to maintain his family consisting of eight members all the year round. Apart from this, there was no irrigation facility for growing of any second crop during winter season. Consequently, Haldar would hire a country boat from his neighbor and go to the river to catch crab and fish with his elder son and wife in order to provide food and fulfill the basic needs of his family.
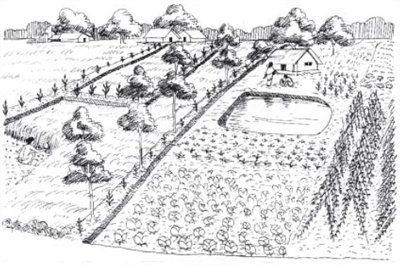
Schematic representation of the farmer derived traditional landshaping approach (on the left side) improved SRAN / DWHH landshaping approach ( on the right side)
ENTERPRISE & ASSETS MAP OF KAIKHALI -4 VILLAG
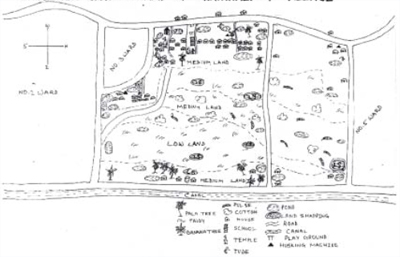
Farmer representation of assets in different land categories
Realizing the benefits of land shaping programme from the villagers of Kaikhali Island, Haldar approached SRAN in 2000-2001 with the intention of adopting such technology. SRAN extended ? financial and technical assistance to him. He implemented one land shaping unit in his 0.26 ha land. After land shaping was completed, he got a pond with an area of 0.05 ha. He strengthened the pond embankment (area 0.01 ha) with the soil from the pond and raised his low-lying land of area 0.20 ha to an height of 1.6 ft. On
implementation of this technology, he was able to grow high yielding variety of rice in a scientific way and harvested nine quintals and 60 kilogram of rice and earn net income of Rs.1,764/-. Besides, having irrigation facility from the pond where water is stored during monsoon, he can cultivate vegetables in winter season keeping in view the demand in the market. The pond is utilized for irrigation as well as fish and prawn culture. The embankment of the pond is also used for banana cultivation which fetches an additional income of Rs. 540/- annually.
The utilization of his land all the year round and the net income from there are explained in the following tables. It is observed that his net income has increased to the tune of 30 times. Now Haldar is able to manage square meals every day for his family. . Besides, due to engagement of his family members in his own land, he has stopped catching crab and fish from the river.
Table - I: Increase in land area
| Before Land Shaping | After Land Shaping | |
| Total Land = (0.26 ha) | Raised Land Shaping Pond Area Embankment | = 0.2 ha. = 0.05 ha. = 0.01 ha. |
| Land situation = Low Irrigation facilities = Nil | Land situation Irrigation facilities | = High = Available |
Table . II: Agricultural yield and income from 0.26 ha. of land before LSP
| Name of the Crop | Total yield at 0.26 ha land area | Value of produce Rs. | Cost of cultivation Rs. | Net income |
| Kharif Season | Paddy | |||
| Local Aman Paddy | 480 kg. x Rs. By product straw 2 kahan* Rs.150/ | 1,920 300 Total = Rs.2,220 4 | Seed 16 kg. x 6/= 96 250 22 Labor for weeding, transplanting, harvesting & threshing 22 x 60/= 1,320 Total = 1,666 Ploughing 2.5 hours x 100/- = | Rs.554 |
| Rabi Season | No crop cultivation | nil | nil | Income Nil |
* Kahan is a local unit equals to about 2.5 quintals
Table . III: Agricultural yield and resultant income from 0.20 ha land area 0.05 ha pond area, 0.013 ha pond embankment after LSP.
Agricultural yield and income from 0.2 ha raised land during Kharif Season
| Season | Name of the Crop | Total yield at 0.20 ha land area | Value of produce Rs. | Cost of cultivation Rs. | Net income Rs. |
| Kharif | HYV Paddy Pankaj By product straw | 960 kg x Rs.43 Kahan x Rs. 80 | 3,840 240 | Seed 15 kg x Rs. 8/=120 Ploughing 2.15 hours x100/-=225 Labour for Transplanting weeding, Harvesting and Threshing etc. 20 labours x Rs. 60/=1,200 Fertilizer Urea 36 kg. x Rs. 5/=180 S.S.P. 50 kg. x Rs. 4=200 M.O.P. 13 kg. x Rs. 7 =91 Pesticide = 300 | |
| Total | Rs.4,080 | Rs.1,764 |
Table . IV: Agricultural yield and income from 0.20 ha land area during Rabi Season
| Season | Name of the Crop | Total yield at 0.20 ha land area | Value of produce Rs. | Cost of cultivation Rs. | Net income Rs. | |
| Rabi | Okra | 4000 kg. x Rs. 5/- | Rs.20,000 | Seed - 4 Kg. x Rs. 900/ Land preparation 4 hours x Rs. 100/Fertilizer and Pesticide Organic Manure Urea 40 Kg. x Rs. 5/S.S.P. 50 Kg. x Rs. 4/M.O.P. 15 Kg. x Rs. 7/Pesticide | = 3,600 = 400 = 500 = 200 = 200 = 105 = 1000 | |
| Total | Rs.20,000 | Total Rs. 8,405 | Rs.11,595 |
Table . V: Additional income from pond embankment (0.013 ha.) area.
| Season | Name of Crop | Total yield at 0.20 ha. Land area | Value of Produce | Cost of Cultivation | Net Income |
| Round the year | Green Banana | 15 Bunch x Rs. 80 | Rs. 1,200/ | Sucker 40 Pcs. x Rs. 5 = 200 Labour 6 x 60 = 360 Manure & fertilizer = 100 | |
| Total 1,200 | Total Rs. 660 | Rs.540 |
Table . VI: Yield and income from fish culture in 0.05 ha pond area
| Season | Fish | Prawn | Total yield Kgs. | Value of Produce | Cost of Cultivation | Net Income | |
| June. March | IMC | M. Rosen-Bergii | 55 Kg. x Rs. 40/8 Kg. x Rs. 200/ | 2,200.00 1,600.00 | Fish fingerlings 4 x Kg. x 50 Prawn200pcs. x 3 Rs Fishfeed LaborCharge | = 200 = 600 = 400 = 400 |
|
| Total | Rs.3,800 | Total Rs. | 1,600 | Rs.2,200 |
Table VII: Green Manure Cultivation for Manuring
| Season | Name of the Crop | Yield | Cost of Cultivation |
| Pre Kharif | Sesbania | Green Manure 10 Ton. (Approx.) | Seed 10 kg x 5 Rs = 50 Land preparation = 2 hours x Rs.100 = 200 |
| Total Rs. 250/ |
Table VIII : Net income and comparative economics from 0.20 ha land, 0.05 ha pond, area of 0.013 ha pond embankment after LSP
| Before Shaping | After Land Shaping Programme Land | ||||
| Net income Rs. | Kharif season Rs. | Rabi season Rs. | Pond embankment Rs. | Pond Rs. | Net income Rs. |
| 554 | 1,76 | 411,595 | 540 | 2200 | 16,099
|
The income of the farmer has increased to the tune of 30 times over before Land Shaping Programme

Taken From Best Practices in Water Management-Case Studies from Rural India-2005 German Agro Action, 2005. We would like to thank German Agro Action for very kindly sharing the case studies for the portal.