To accelerate the efforts to achieve universal sanitation coverage and to put focus on sanitation, the Prime Minister of India launched the Swachh Bharat Mission on 2 October, 2014. Following this, guidelines for the implementation of the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) were issued by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Government of India (GoI).
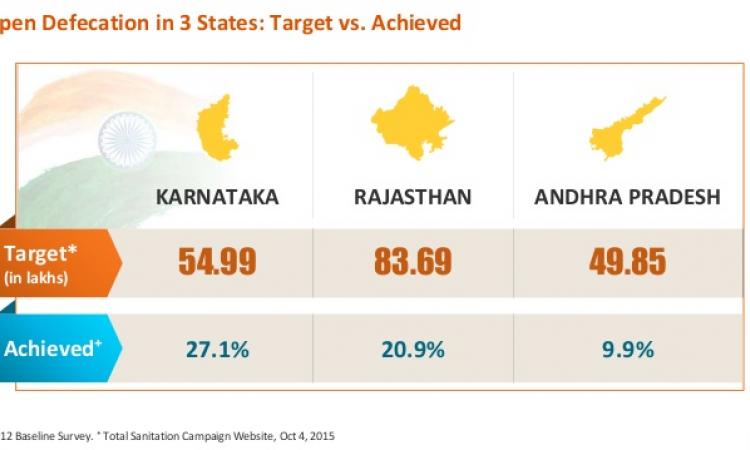
The guidelines issued by GoI are operationalised by different States in varied ways. As a follow-up to its work on behaviour change communication and decongesting supply side bottlenecks, Arghyam undertook a high level process mapping including operational procedures, information systems, fund flow mechanisms, and human resources, involved with the household toilet construction aspect of SBM (Rural). The study was conducted by FourthLion, a Bangalore based development consulting firm that seeks to create impact at scale by leveraging the government machinery, in the three States of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan.
FourthLion adopted a field-cum‐forum methodology for the study that was conducted between July and October, 2015. The team followed a cyclical work-plan of spending time in the field, convening and consolidating observations and then going back to field. This was to ensure that the areas of enquiry and discussions were grounded in reality. For each of the states, a report entailing the current operation of the scheme, analysis of problems and bottlenecks, recommendations for changes and improvements, some good practices observed at different levels was produced. The broad findings from the study are available for download.
Enhancing the implementation of SBM (Gramin)
Enhancing the Implementation of Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin) in Karnataka